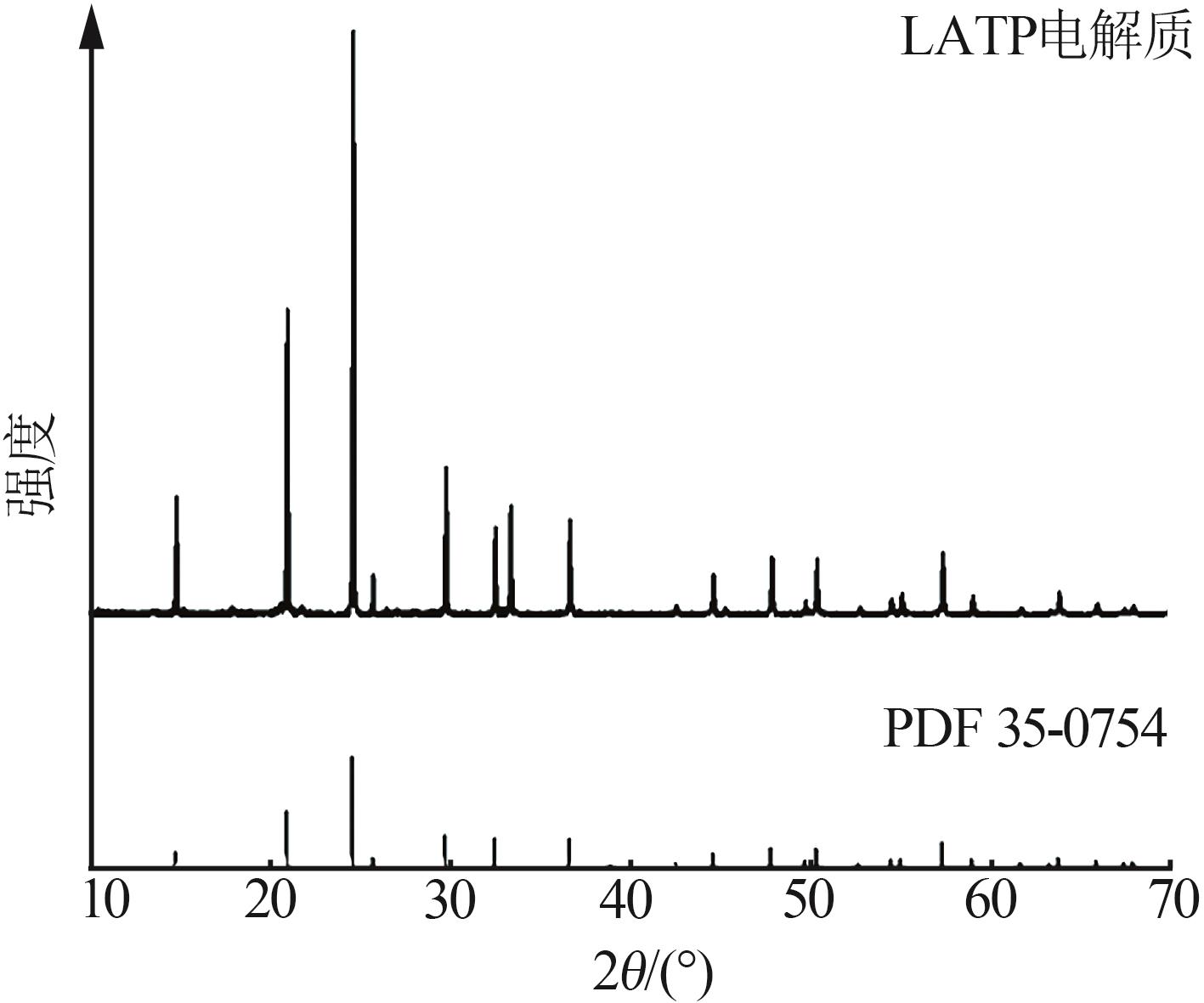
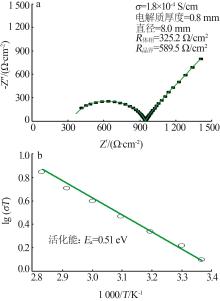
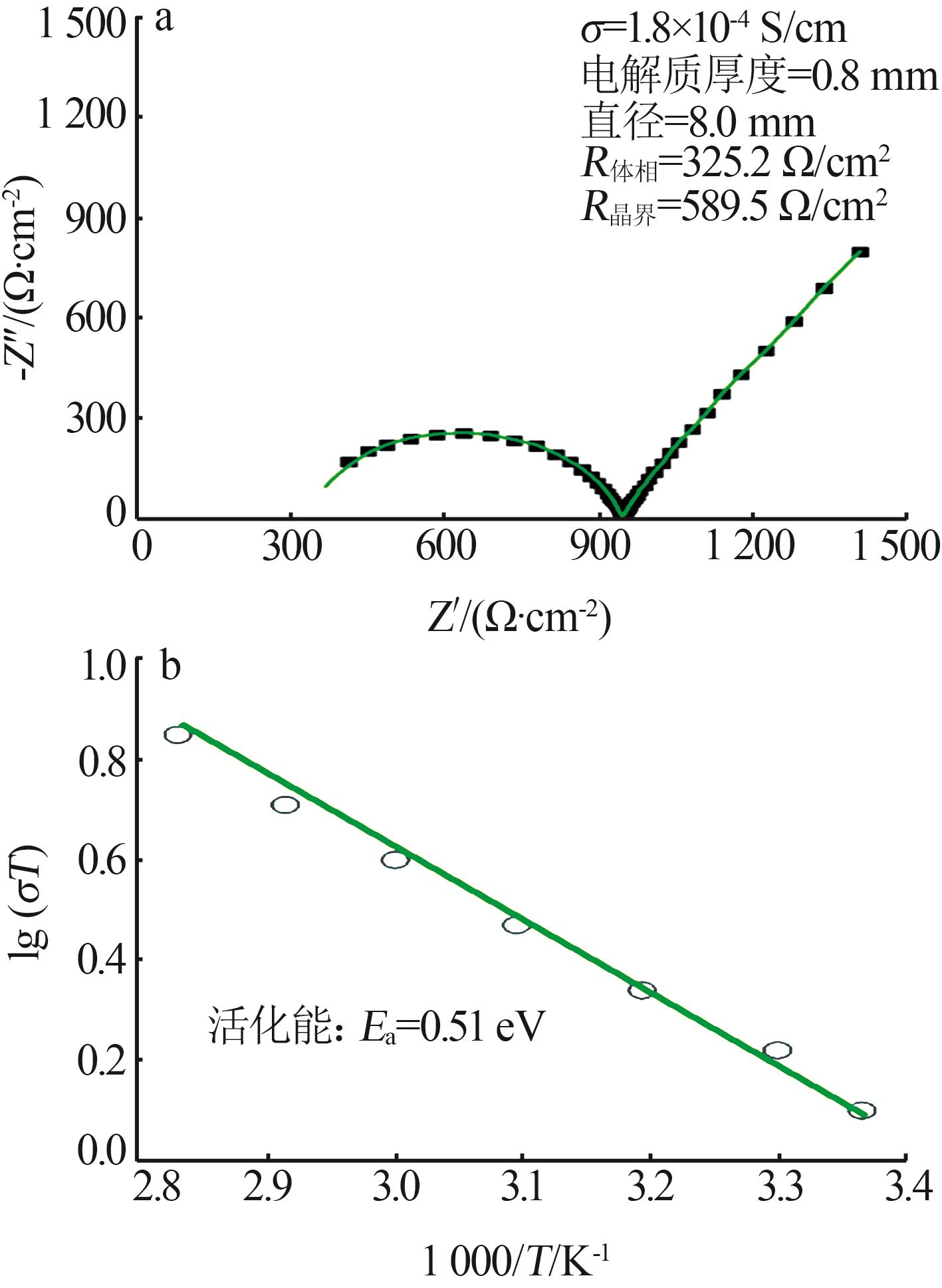
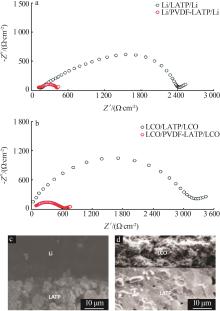
| 1 |
ZHU Yizhou, HE Xingfeng, MO Yifei. Origin of outstanding stability in the lithium solid electrolyte materials:Insights from thermodynamic analyses based on first-principles calculations[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(42):23685-23693.
|
| 2 |
DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid:A battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058):928-935.
doi: 10.1126/science.1212741
|
| 3 |
韩佳欢, 乜贞, 方朝合, 等. 中国锂资源供需现状分析[J]. 无机盐工业, 2021, 53(12):61-66.
|
|
HAN Jiahuan, NIE Zhen, FANG Chaohe, et al. Analysis of existing circumstance of supply and demand on China′s lithium resourc-es[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(12):61-66.
|
| 4 |
SWAMY T, CHEN Xinwei, CHIANG Y M. Electrochemical redox behavior of Li ion conducting sulfide solid electrolytes[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(3):707-713.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b03420
|
| 5 |
WINTER M, BARNETT B, XU Kang. Before Li ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(23):11433-11456.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00422
pmid: 30500179
|
| 6 |
WANG Shuo, BAI Qiang, NOLAN A M, et al. Lithium chlorides and bromides as promising solid-state chemistries for fast ion conductors with good electrochemical stability[J]. Angewandte Chemie(International Ed.in English), 2019, 58(24):8039-8043.
|
| 7 |
ZHANG Zhizhen, SHAO Yuanjun, LOTSCH B, et al. New horizons for inorganic solid state ion conductors[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(8):1945-1976.
|
| 8 |
LI Xiaona, LIANG Jianwen, CHEN Ning, et al. Water-mediated synthesis of a superionic halide solid electrolyte[J]. Angewandte Chemie(International Ed.in English), 2019, 58(46):16427-16432.
|
| 9 |
LI Jizhou, LI Shaofeng, ZHANG Yuxin, et al. Multiphase,multiscale chemomechanics at extreme low temperatures:Battery electrodes for operation in a wide temperature range[J]. Adv.Energy Mater., 2021, 11(37):2102122.
|
| 10 |
ZHAO Ning, KHOKHAR W, BI Zhijie, et al. Solid garnet batteries[J]. Joule, 2019, 3(5):1190-1199.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2019.03.019
|
| 11 |
CHEN Rusong, YAO Chunxia, YANG Qi, et al. Enhancing the thermal stability of NASICON solid electrolyte pellets against metallic lithium by defect modification[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(16):18743-18749.
|
| 12 |
XIA Qiuying, NI Mingzhu, CHEN Minghua, et al. Low-temperature synthesized self-supported single-crystalline LiCoO2 nanoflake arrays as advanced 3D cathodes for flexible lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(11):6187-6196.
doi: 10.1039/c9ta00351g
|
| 13 |
LUO Wei, GONG Yunhui, ZHU Yizhou, et al. Transition from superlithiophobicity to superlithiophilicity of garnet solid-state electrolyte[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(37):12258-12262.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b06777
pmid: 27570205
|
| 14 |
CHEN Shaojie, NIE Zhiwei, TIAN Feifei, et al. The influence of surface chemistry on critical current density for garnet electroly-te[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(23):2113318.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v32.23
|
| 15 |
HAN Fudong, ZHU Yizhou, HE Xingfeng, et al. Electrochemical stability of Li10GeP2S12 and Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolytes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(8):1501590.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v6.8
|
| 16 |
LIU Ting, ZHANG Yibo, ZHANG Xue, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of bulk type oxide ceramic lithium batteries enabled by interface modification[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(11):4649-4657.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA06833F
|
| 17 |
DUAN Hui, CHEN Wanping, FAN Min, et al. Building an air stable and lithium deposition regulable garnet interface from moderate-temperature conversion chemistry[J]. Angewandte Chemie(International Ed.in English), 2020, 59(29):12069-12075.
|