Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (10): 100-105.doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0707
• Environment·Health·Safety • Previous Articles Next Articles
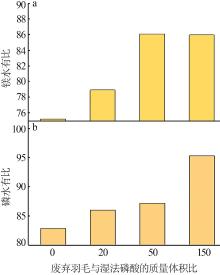
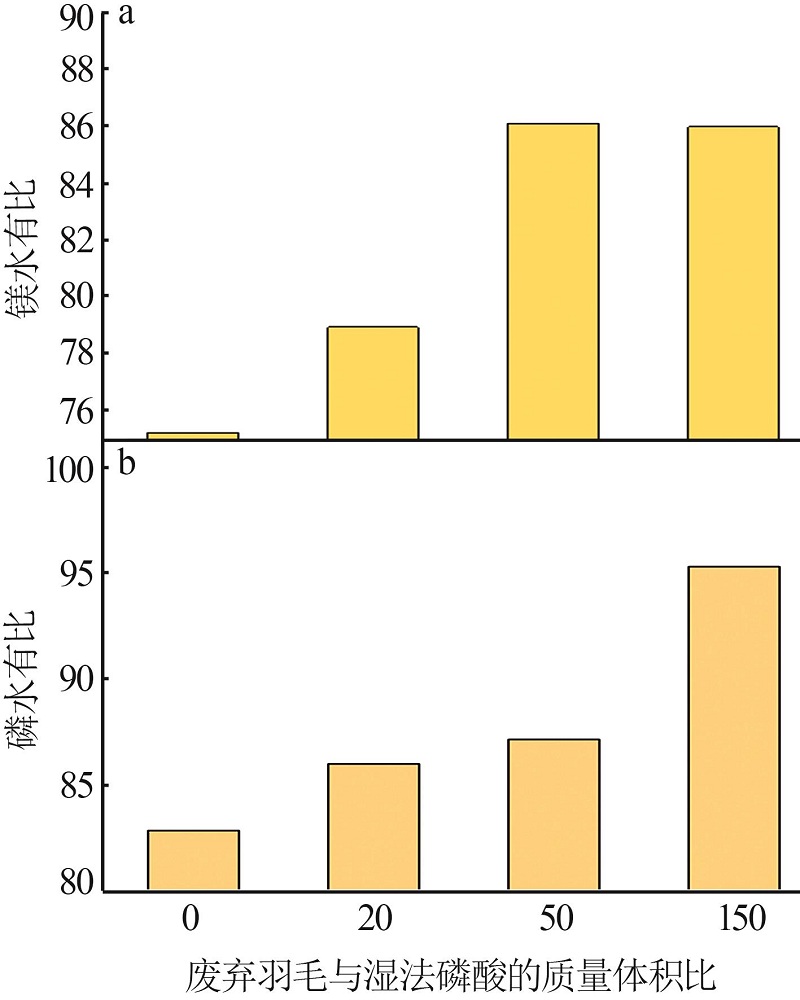
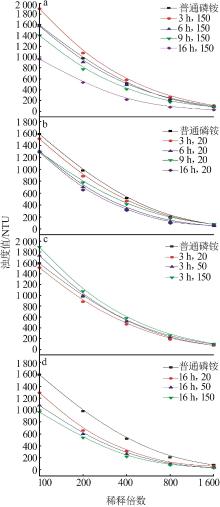
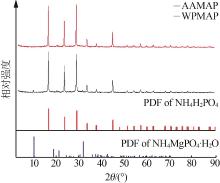
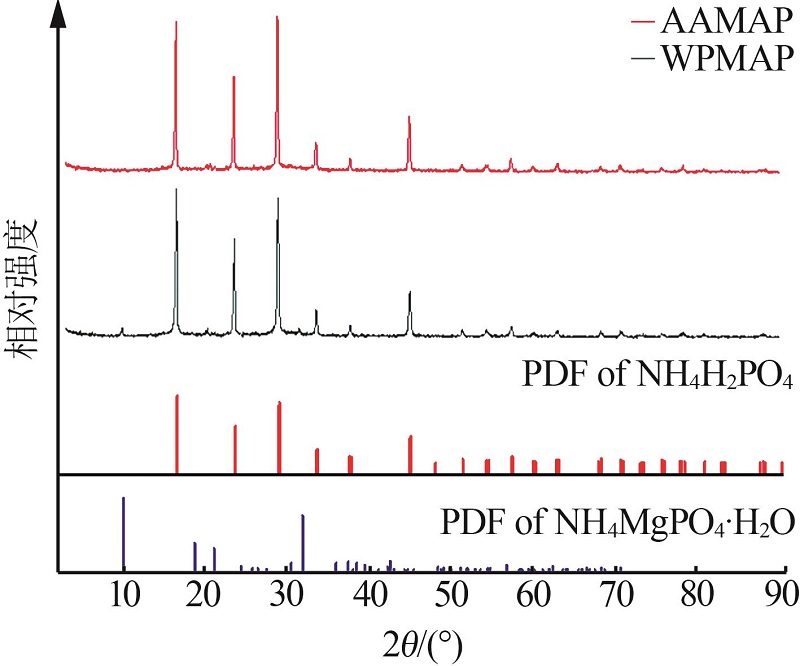
Preparation of monoammonium phosphate containing amino acid from waste feathers by in situ acid hydrolysis of wet process of phosphoric acid
HE Fuduo( ), YUAN Yifan, ZHOU Xiaohou, XU Lu, SUN Chongqing, WANG Xinlong(
), YUAN Yifan, ZHOU Xiaohou, XU Lu, SUN Chongqing, WANG Xinlong( ), XU Dehua
), XU Dehua
- Ministry of Education Research Center for Comprehensive Utilization and Clean Processing Engineering ofPhosphorus Resources,School of Chemical Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,China