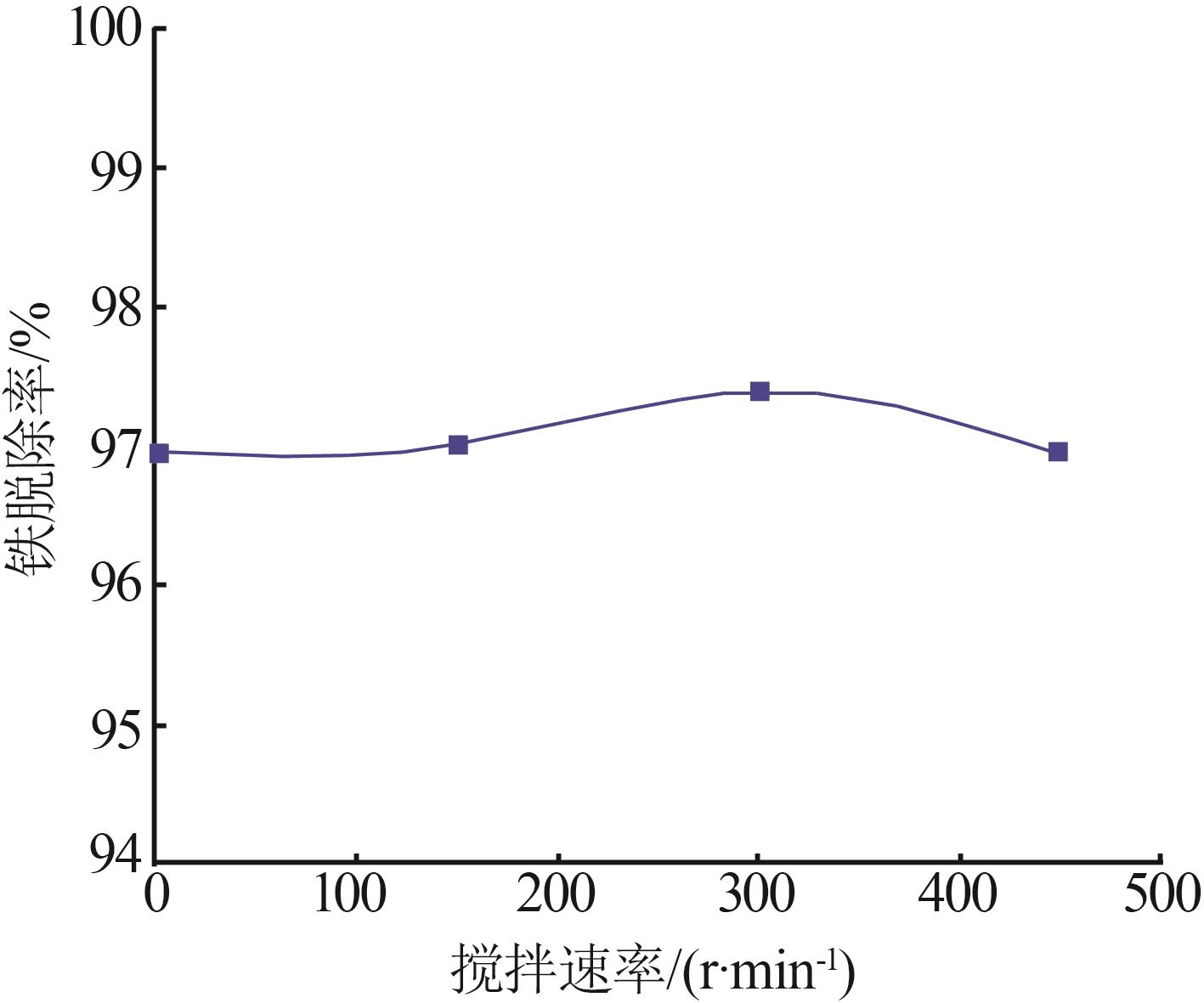
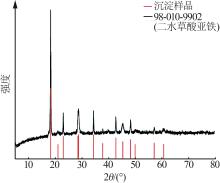
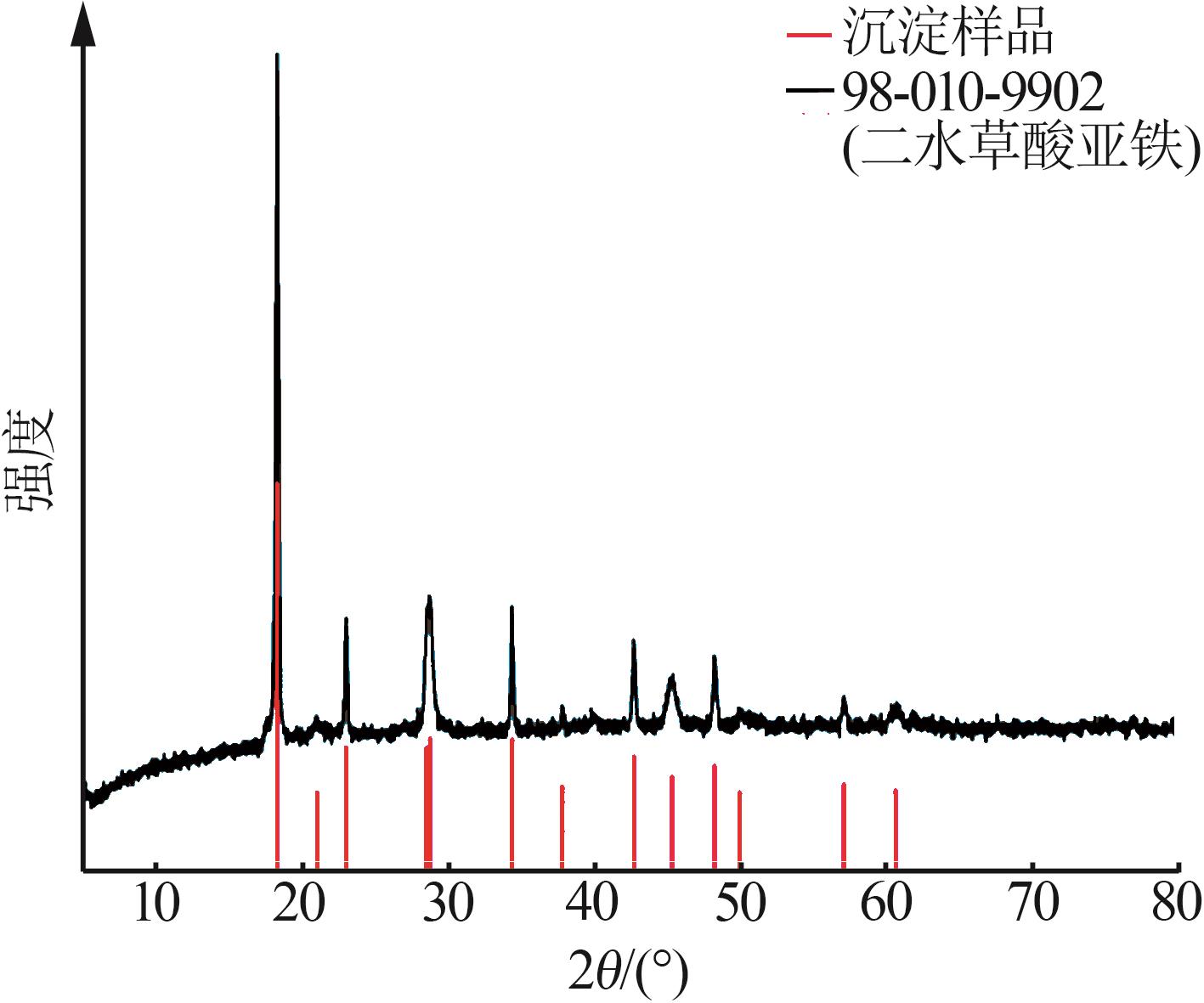
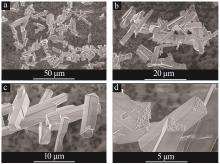
| 1 |
冯海涛,董亚萍,梁建,等.基于电化学法的铬盐清洁生产工艺研究[J].盐湖研究,2019,27(4):9-17.
|
|
FENG Haitao, DONG Yaping, LIANG Jian,et al.Study on the green production process of chromate based on electrochemical method[J].Journal of Salt Lake Research,2019,27(4):9-17.
|
| 2 |
DERABLA T, AFFOUNE A M, CHELAGHMIA M L.Effects of PEG,PVP and SDS on the properties of chromium coatings prepared from trivalent chromium chloride baths using experimental design and multi-response optimisation[J].Surface Engineering and Applied Electrochemistry,2019,55(3):304-316.
|
| 3 |
任丽丽.高效三价铬电镀工艺研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2011.
|
|
REN Lili.Technology of effective trivalent chromium plating[D].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology,2011.
|
| 4 |
BARKER W E, KENNEDY D J.The reduction of acetylene to ethylene by chromous chloride[J].Transactions of the Electrochemical Society,1947,92(1):391.
|
| 5 |
纪柱.铬盐发展方向:开发铬盐新产品、新用途[J].无机盐工业,2014,46(10):1-7.
|
|
JI Zhu.Development direction of chromium salts:Development of new chromium products and uses[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2014,46(10):1-7.
|
| 6 |
ZHENG S, ZHANG Y, LI Z,et al.Green metallurgical processing of chromite[J].Hydrometallurgy,2006,82(3/4):157-163.
|
| 7 |
张懿,李佐虎,王志宽,等.绿色化学与铬盐工业的新一代产业革命[J].化学进展,1998,10(2):172-178.
|
|
ZHANG Yi, LI Zuohu, WANG Zhikuan,et al.Green chemistry and new revolution of chromic salts industry[J].Progress in Chemistry,1998,10(2):172-178.
|
| 8 |
梅海军,王劲松,宋卫国,等.铬酸盐的高效、节能、清洁的制造方法:中国,101508466A[P].2009-08-19.
|
| 9 |
冯海涛,董亚萍,李武,等.电合成重铬酸钠用析氧阳极的研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2011,43(11):9-11.
|
|
FENG Haitao, DONG Yaping, LI Wu,et al.Research progress in oxygen evolution anodes used in electrosynthesis of sodium dichromate[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2011,43(11):9-11.
|
| 10 |
TIAN Sen.Production and characterization of chromium oxide (Cr2O3) via a facile combination of electrooxidation and calcination[J].International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2019:8805-8818.
|
| 11 |
李超.离子膜电解制备金属铬粉及阳极电溶高碳铬铁的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2014.
|
|
LI Chao.Research on anode eletrochemical dissolution of high-carbon ferrochrome and electrodeposition of chromium in an ion-exchange membrane reactor[D].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Tech-nology,2014.
|
| 12 |
董亚萍,冯海涛,李武,等.电解铬铁联合生产氧化铬绿、氧化铁红和高纯铬酸盐的方法:中国,107523839B[P].2019-03- 26.
|
| 13 |
冯海涛,董亚萍,李波,等.>利用铬铁制备高纯度铬酸盐的方法:中国,107587155B[P].2019-06-14.
|
| 14 |
冯海涛,李波,董亚萍,等.利用铬铁制备氧化铬绿的方法:中国,107585788B[P].2019-06-14.
|
| 15 |
魏峰,狄蕊,杜锋,等.含铬污泥酸浸出液中铬离子和铁离子的分离[J].检验检疫学刊,2016,26(4):14-16.
|
|
WEI Feng, DI Rui, DU Feng,et al.Study on separation of chromium ion and iron ion in acid extracting solution of chromium sludge[J].Journal of Inspection and Quarantine,2016,26(4):14-16.
|
| 16 |
刘佳宁,姜茂发,李昱彤,等.针铁矿法分离铬铁矿硫酸浸出液中Cr3+与Fe3+ [J].过程工程学报,2015,15(2):242-246.
|
|
LIU Jianing, JIANG Maofa, LI Yutong,et al.Separation of Cr3+ and Fe3+ from sulphuric acid leaching solution of chromite by goethite method[J].The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering,2015,15(2):242-246.
|
| 17 |
焦晓斌,段小维,段宏志.锌焙砂浸出过程中两渣分离的探索与实践[J].中国有色冶金,2016,45(3):6-9,34.
|
|
JIAO Xiaobin, DUAN Xiaowei, DUAN Hongzhi.Explorative study and practice on Pb-Ag residue and jarosite residue separation during zinc calcine leaching[J].China Nonferrous Metallurgy,2016,45(3):6-9,34.
|
| 18 |
张魁芳,刘志强,曹洪杨,等.用N235从富铁高酸度硫酸浸出液中萃取除铁[J].中国有色金属学报,2015,25(5):1370-1377.
|
|
ZHANG Kuifang, LIU Zhiqiang, CAO Hongyang,et al.Removal of Fe3+ from iron rich and high acidity sulfuric acid leaching liquid by extraction of N235[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2015,25(5):1370-1377.
|
| 19 |
秦险峰,全学军,叶鹏,等.铬铁矿酸浸过程强化及铬铁分离研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(6):13-19.
|
|
QIN Xianfeng, QUAN Xuejun, YE Peng,et al.Research progress of process intensification of acid leaching technology from chromite ore and separation of chromium-iron[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(6):13-19.
|
| 20 |
赵青.碱式硫酸铬清洁制备工艺的基础研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2015.
|
|
ZHAO Qing.Fundamental research on the cleaner preparation process of basic chromium sulfate[D].Shenyang:Northeastern University,2015.
|
| 21 |
ZHAO Qing, LIU Chengjun, YANG Dapeng,et al.A cleaner method for preparation of chromium oxide from chromite[J].Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2017,105:91-100.
|
| 22 |
王亲猛.碳素铬铁中元素有效分离及综合利用研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2011.
|
|
WANG Qinmeng.Study on effective separation and comprehensive utilization of elements from carbon ferrochromium[D].Chan-gsha:Central South University,2011.
|
 ), LI Xinqian1,2,3, FENG Haitao1,2(
), LI Xinqian1,2,3, FENG Haitao1,2( ), LI Bo1,2, NIU Zhengrong1,2, DONG Yaping1,2
), LI Bo1,2, NIU Zhengrong1,2, DONG Yaping1,2