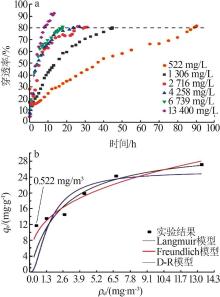
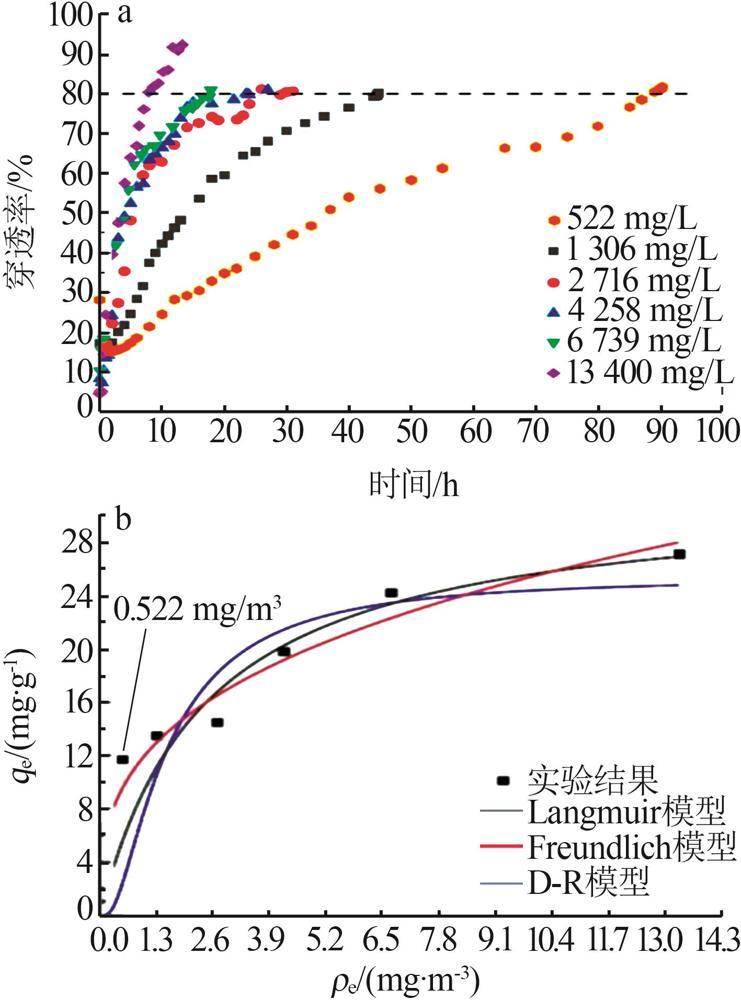
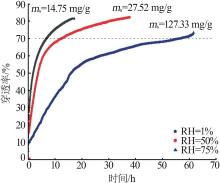
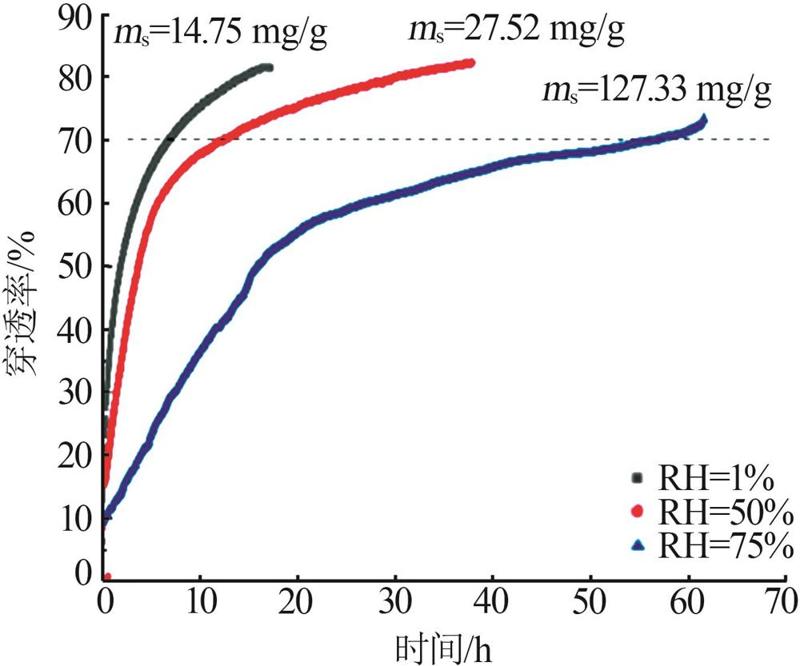
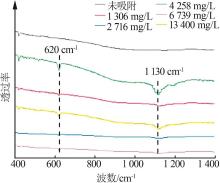
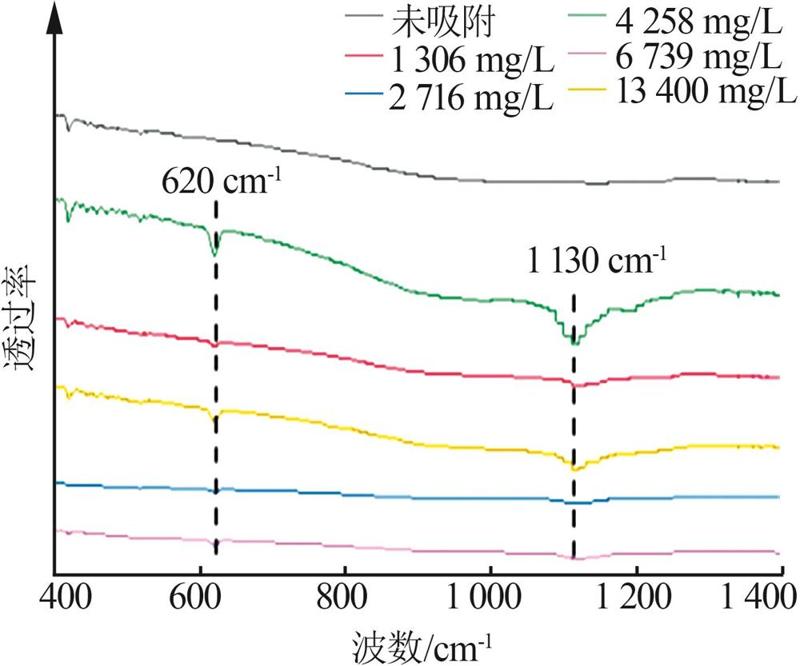
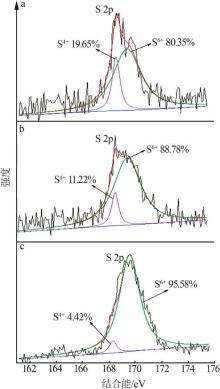
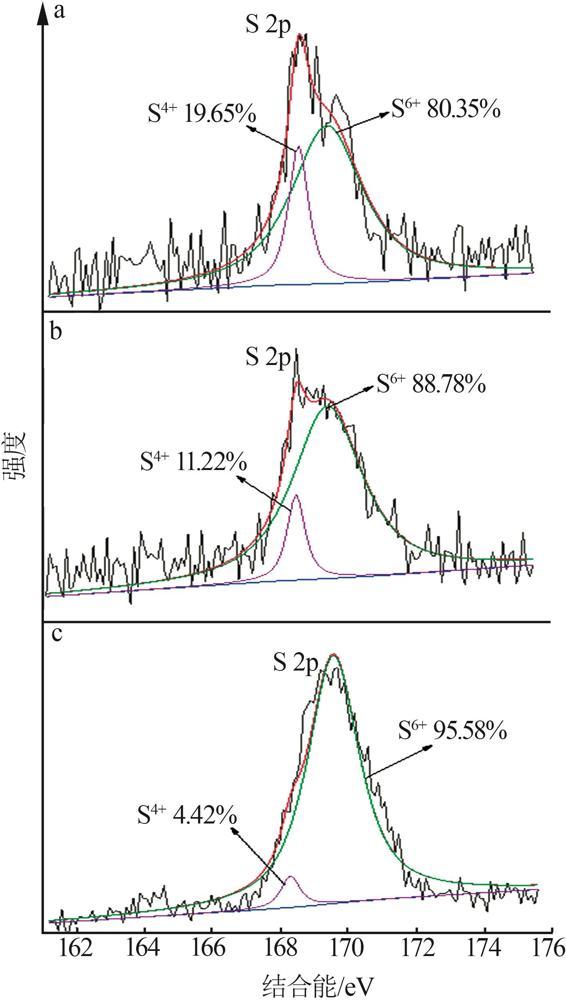
| [1] |
HENDRYX M, LUO Juhua, CHOJENTA C, et al.Air pollution exposures from multiple point sources and risk of incident chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) and asthma[J].Environmental Research,2019,179.Doi:10.1016/j.envres.2019.108783.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108783.
|
| [2] |
LIN S Y, JU S W, LIN Chengli, et al.Air pollutants and subsequent risk of chronic kidney disease and end⁃stage renal disease:A population⁃based cohort study[J].Environmental Pollution,2020,261.Doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114154.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114154.
|
| [3] |
王建行,赵颖颖,李佳慧,等.二氧化碳的捕集、固定与利用的研究进展[J].无机盐工业,2020,52(4):12-17.
|
|
WANG Jianhang, ZHAO Yingying, LI Jiahui, et al.Research progress of carbon dioxide capture,fixation and utilization[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2020,52(4):12-17.
|
| [4] |
BUREŠ R, KLAJMON M, FOJT J, et al.Artificial patination of copper and copper alloys in wet atmosphere with increased content of SO2 [J].Coatings,2019,9(12).Doi:10.3390/coatings9120837.
doi: 10.3390/coatings9120837.
|
| [5] |
ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Jianshun, SCHMIDT R, et al.Effects of moisture content,temperature and pollutant mixture on atmosp⁃heric corrosion of copper and silver and implications for the environmental design of data centers(RP-1755)[J].Science and Technology for the Built Environment,2020,26(4):567-586.
|
| [6] |
RICE D W, PETERSON P, RIGBY E B, et al.Atmospheric corrosion of copper and silver[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,1981,128(2):275-284.
|
| [7] |
FERRERO L, SANGIORGI G, FERRINI B S, et al.Aerosol corrosion prevention and energy⁃saving strategies in the design of green data centers[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(8):3856-3864.
|
| [8] |
苏少龙,曲晓龙,钟读乐,等.工业烟气脱硫工艺进展[J].无机盐工业,2019,51(11):13-15,87.
|
|
SU Shaolong, QU Xiaolong, ZHONG Dule, et al.Progress of industrial flue gas desulfurization process[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2019,51(11):13-15,87.
|
| [9] |
LI Jianjun, KOBAYASHI N, HU Yongqi.The activated coke preparation for SO2 adsorption by using flue gas from coal power plant[J].Chemical Engineering and Processing:Process Intensification,2008,47(1):118-127.
|
| [10] |
李天杰.硫酸锌溶液脱除钙镁试验及生产应用[J].无机盐工业,2012,44(12):38-39.
|
|
LI Tianjie.Experiment and production application of removal of Ca2+ and Mg2+ from zinc sulphate solution[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2012,44(12):38-39.
|
| [11] |
SEVERA G, HEAD J, BETHUNE K, et al.Comparative studies of low concentration SO2 and NO2 sorption by activated carbon supported[C2mim][Ac]and KOH sorbents[J].Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2018,6(1):718-727.
|
| [12] |
ZHANG Yaping, YUE Xiupeng, XU Weiwei, et al.Amino modification of rice straw⁃derived biochar for enhancing its cadmium(Ⅱ) ions adsorption from water[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,379.Doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120783.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120783.
|
| [13] |
BAKER H M.Removal of lead ions from waste water using modified Jordanian zeolite[J].Chemical Science International Journal,2020:29(8):19-30.
|
| [14] |
ZHOU Wu, GUAN Zheng, ZHAO Mengge, et al.Characteristics and mechanism of toluene removal from gas by novelty array double dielectric barrier discharge combined with TiO2/Al2O3 catalyst[J].Chemosphere,2019,226:766-773.
|
| [15] |
WU Yue, LIU Yu, DOU Ruidi, et al.Larger pore volume tetrapheny⁃
doi: 101002/app.48572
|
|
ladamantane⁃based hybrid porous polymers:Facile friedel⁃crafts preparation,CO2 capture,and Rhodamine B removal properties[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2020,137(16).Doi:101002/app.485721002/app.48572.
doi: 101002/app.48572
|
| [16] |
刘纪江.硅胶变压-变温耦合吸附处理尾气中极性二元VOCs组分[D].天津:天津大学,2018.
|
|
LIU Jijiang.Treatment of binary polar VOCs from off⁃gas by silica gel using coupled pressure and temperature swing adsorption[D].Tianjin:Tianjin University,2018.
|
| [17] |
SHIUE A, DEN W, KANG Yuhao, et al.Validation and application of adsorption breakthrough models for the chemical filters used in the make⁃up air unit(MAU) of a cleanroom[J].Building and Environment,2011,46(2):468-477.
|
| [18] |
PEI Jingjing, ZHANG J S.Determination of adsorption isotherm and diffusion coefficient of toluene on activated carbon at low concentrations[J].Building and Environment,2012,48:66-76.
|
| [19] |
ATANES E, NIETO-MÁRQUEZ A, CAMBRA A, et al.Adsorption of SO2 onto waste cork powder⁃derived activated carbons[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,211-212:60-67.
|
| [20] |
HU Qingyuan, LU Yunfeng, MEISNER G P.Preparation of nanoporous carbon particles and their cryogenic hydrogen storage capacities[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2008,112(5):1516-1523.
|
| [21] |
金青青,梁晓怿,张佳楠,等.改性球形活性炭对氨气吸附性能的研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(4):61-66.
|
|
JIN Qingqing, LIANG Xiaoyi, ZHANG Jianan, et al.Study on adsorption performance of modified spherical activated carbon for ammonia[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(4):61-66.
|
| [22] |
SUN Fei, GAO Jihui, LIU Xin, et al.A systematic investigation of SO2 removal dynamics by coal⁃based activated cokes:The synergic enhancement effect of hierarchical pore configuration and gas components[J].Applied Surface Science,2015,357:1895-1901.
|
| [23] |
LU H, JANIN E, DÁVILA M, et al.Adsorption of SO2 on Cu(100) and Cu(100)-c(2×2)-O surfaces studied with photoelectron spectroscopy[J].Vacuum,1998,49(3):171-174.
|
| [24] |
庄海波,杨林,邓强,等.离子交换法脱除磷酸中锰离子的动态吸附研究[J].无机盐工业,2021,53(1):18-23.
|
|
ZHUANG Haibo, YANG Lin, DENG Qiang, et al.Study on dynamic adsorption of Mn2+ from phosphoric acid by ion exchange technology[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2021,53(1):18-23.
|
| [25] |
汪鹏,赵磊,刘志禹,等.活性炭材料变压吸附SO2的研究[J].应用化工,2020,49(11):2722-2727.
|
|
WANG Peng, ZHAO Lei, LIU Zhiyu, et al.Research on active carbon materials for SO2 pressure swing adsorption[J].Applied Chemical Industry,2020,49(11):2722-2727.
|
| [26] |
BAI B C, LEE C W, LEE Y S, et al.Modification of textural properties of CuO-supported activated carbon fibers for SO2 adsorption based on electrical investigation[J].Materials Chemistry and Physics,2017,200:361-367.
|
| [27] |
AL-GHOUTI M A, DA'ANA D A.Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models:A review[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,393.Doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383.
|
| [28] |
尚方毓,苏小红,胡昉.氧化镁湿法脱硫在硫化碱行业的应用探讨[J].无机盐工业,2016,48(4):50-52.
|
|
SHANG Fangyu, SU Xiaohong, HU Fang.Study on application of magnesium oxide in flue gas desulphurization in alkali sulfide industry[J].Inorganic Chemicals Industry,2016,48(4):50-52.
|
| [29] |
GAO Xiang, LIU Shaojun, ZHANG Yang, et al.Physicochemical properties of metal⁃doped activated carbons and relationship with their performance in the removal of SO2 and NO[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,188(1/2/3):58-66.
|
| [30] |
LISOVSKII A, SEMIAT R, AHARONI C.Adsorption of sulfur dioxide by active carbon treated by nitric acid:I.Effect of the treatment on adsorption of SO2 and extractability of the acid formed[J].Carbon,1997,35(10/11):1639-1643.
|
| [31] |
LIU Fudong, ASAKURA K, HE Hong, et al.Influence of sulfation on iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3 [J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2011,103(3/4):369-377.
|
 ),ZHANG Junjie,LIU Xiangcheng,JIN Wufeng(
),ZHANG Junjie,LIU Xiangcheng,JIN Wufeng( )
)