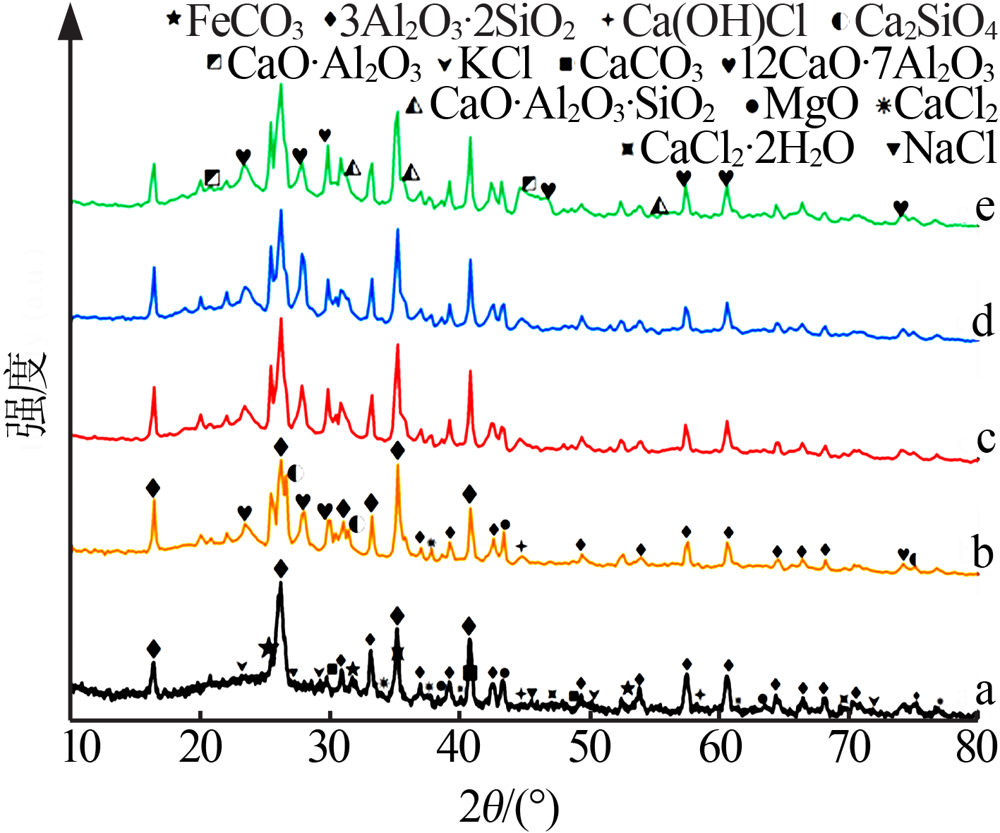
| [1] |
牛耀岚, 胡伟, 朱辉, 等. 燃煤电厂脱硫废水处理方法及零排放技术进展[J]. 长江大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 16(10):72-78.
|
| [2] |
张山山, 王仁雷, 晋银佳, 等. 燃煤电厂脱硫废水零排放处理技术研究应用及进展[J]. 华电技术, 2019, 41(12):25-30.
|
| [3] |
马双忱, 于伟静, 贾绍广, 等. 燃煤电厂脱硫废水处理技术研究与应用进展[J]. 化工进展, 2016, 35(1):255-262.
|
| [4] |
笪春年, 汪海, 徐波, 等. 燃煤电厂煤中氯的迁移和释放特征[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(10):2833-2839.
|
| [5] |
Bie R, Chen P, Song X F, et al. Characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with cement solidification treatment[J]. Journal of The Energy Institute, 2016, 89(4):704-712.
doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2015.04.006
|
| [6] |
Zhu F F, Takaoka M, Shiota K, et al. Chloride chemical form in vari-ous types of fly ash[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(11):3932-3937.
doi: 10.1021/es7031168
|
| [7] |
Pan J R, Huang C, Kuo J J, et al. Recycling MSWI bottom and fly ash as raw materials for Portland cement[J]. Waste Management, 2008, 28(7):1113-1118.
doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2007.04.009
|
| [8] |
Aljerf L. Effect of thermal-cured hydraulic cement admixtures on the mechanical properties of concrete[J]. Interceram-International Ceramic Review, 2015, 64(8):346-356.
doi: 10.1007/BF03401142
|
| [9] |
朱芬芬, 高冈昌辉, 大下和徹, 等. 焚烧飞灰预处理工艺及其无机氯盐的行为研究[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(6):2473-2478.
|
| [10] |
Yang S, Saffarzadeh A, Shimaoka T, et al. Existence of Cl in muni-cipal solid waste incineration bottom ash and dechlorination effect of thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 267:214-220.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.045
|
| [11] |
Zhu F F, Takaoka M, Oshita K, et al. The calcination process in a system for washing,calcinating,and converting treated municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash into raw material for the cement in-dustry[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2011, 61(7):740-746.
|
| [12] |
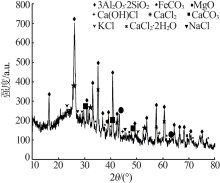
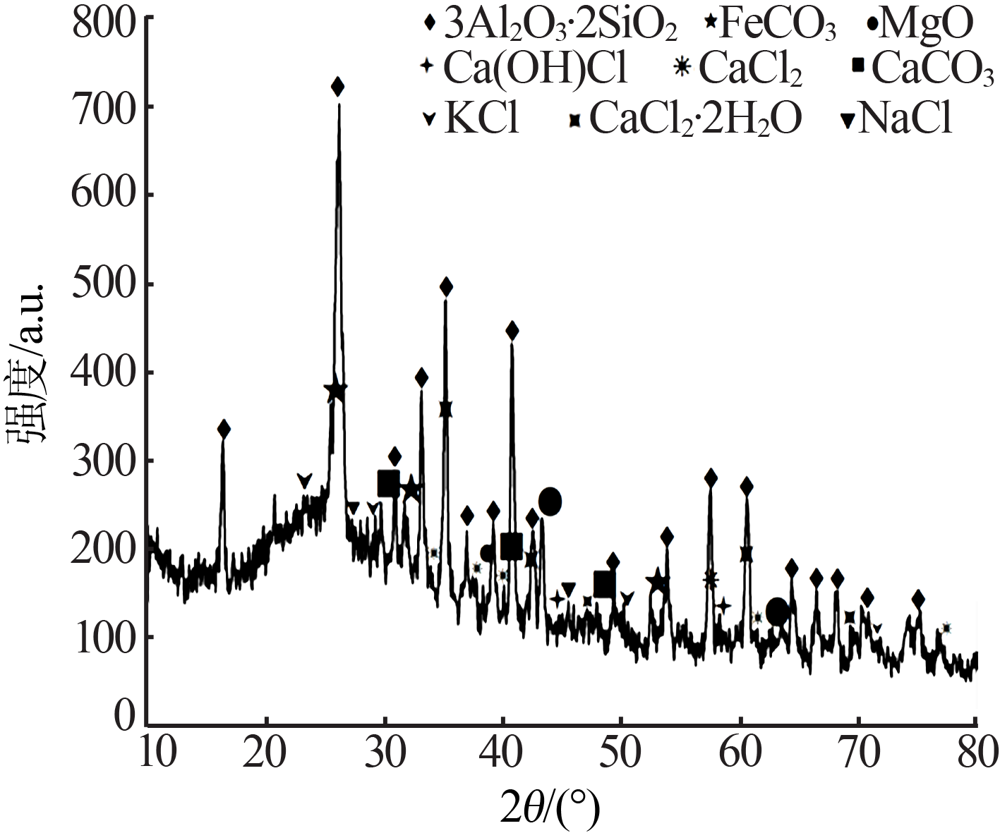
刘韶华. X射线荧光光谱法在煤灰化学成分测定中的应用[J]. 产业与科技论坛, 2015(18):47-48.
|
| [13] |
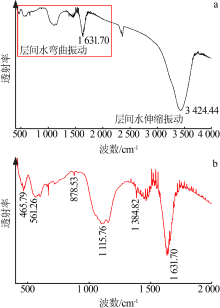
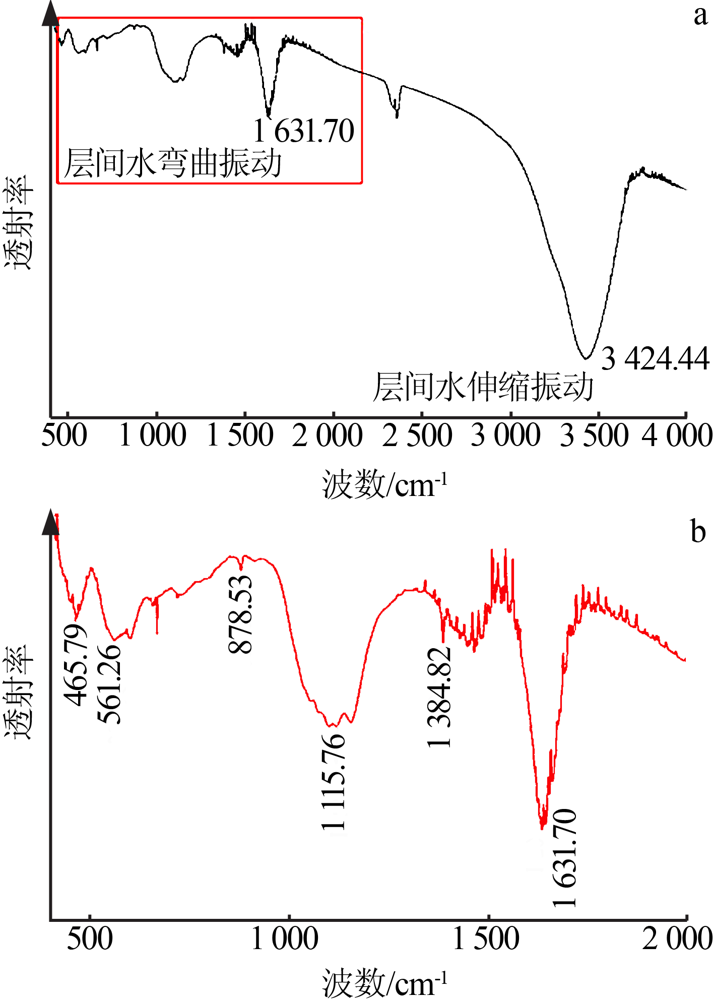
刘云霞, 曾凡桂, 孙蓓蕾, 等. 古交飞灰不同粒径颗粒的XRD及FTIR研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(5):1452-1456.
|
| [14] |
修连存, 郑志忠, 俞正奎, 等. 近红外光谱分析技术在蚀变矿物鉴定中的应用[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(11):1584-1590.
|
| [15] |
才凤, 贾宏新. 离子色谱法测定工业废水中甲酸根、乙酸根和氯离子[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2020, 11(1):219-222.
|
| [16] |
周少玲, 张永. 各种氯离子含量测定方法的适用性探讨及新方法的提出[J]. 热力发电, 2008(7):75-77.
|
| [17] |
王生智, 白亚亚. 工业水氯离子含量测定方法的优化[J]. 石油化工应用, 2012, 31(3):82-83,91.
|
| [18] |
郝志宁. 水中氯离子的测定方法及其研究进展[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2016, 41(5):162-164.
|
| [19] |
刘春香, 谢秋利, 张真真, 等. 原盐中氯离子测定方法的优化[J]. 纯碱工业, 2019(5):22-25.
|
| [20] |
侯玉亭, 马旭, 曹升玲, 等. 南屯煤矿灌浆用粉煤灰的红外光谱特性研究[J]. 煤矿现代化, 2019(1):96-99.
|
| [21] |
陈剑虹, 朱凌建, 华灯鑫. 氯化钠近红外光谱检测技术研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(4):949-952.
|
| [22] |
张彬, 陈剑虹, 焦明星. 氯盐溶液近红外光谱分析研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(7):1840-1843.
|
| [23] |
Zhao K X, Hu Y Y, Tian Y Y, et al. Chlorine removal from MSWI fly ash by thermal treatment:Effects of iron/aluminum additives[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 88:112-121.
|
| [24] |
Cha S C, Spiegel M. Local reactions between NaCl and KCl parti-cles and metal surfaces[J]. Corrosion Engineering,Science and Technology, 2005, 40(3):249-254.
doi: 10.1179/174327805X66317
|
| [25] |
Cha S C, Spiegel M. Local reactions of KCl particles with iron,ni-ckel and chromium surfaces[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2006, 57(2):159-164.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4176
|
| [26] |
Chen W S, Chang F C, Shen Y H, et al. Removal of chloride from MSWI fly ash[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012,237- 238:116-120.
|
 ),Chen Biao1,2,Feng Xiangdong1,2,Chen Hui3,Sun Qing3,Zhang Jian3,Sheng Jiawei3(
),Chen Biao1,2,Feng Xiangdong1,2,Chen Hui3,Sun Qing3,Zhang Jian3,Sheng Jiawei3( )
)