Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 25-28.doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2018-0551
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
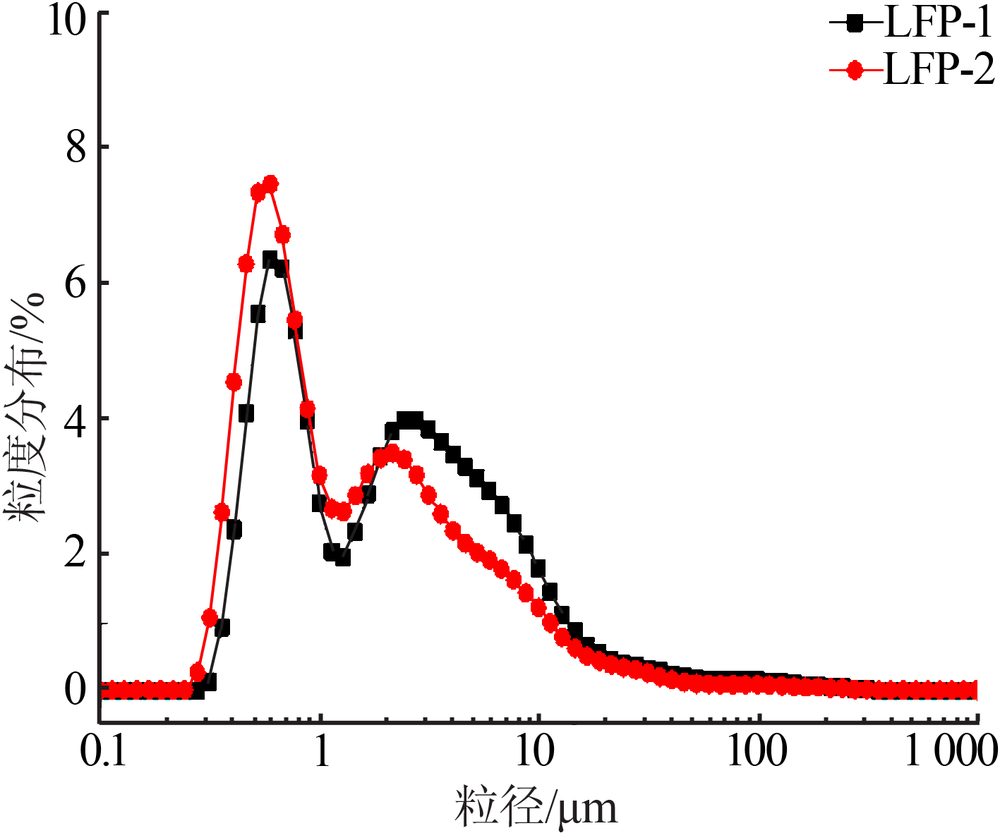
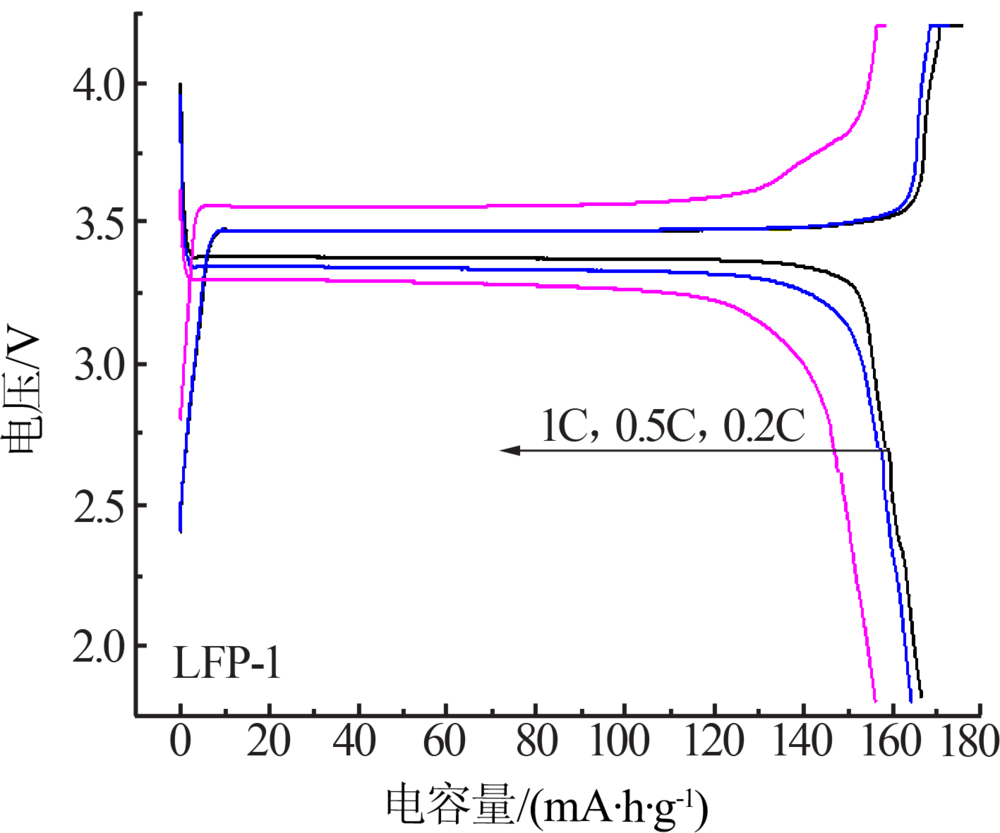
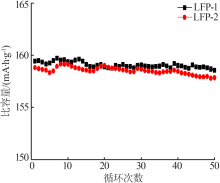
Preparation of spherical lithium iron phosphate material and its 18650 battery test
Chen Lei( ),Zhao Longtao,Chen Zhenyu,Li Guang
),Zhao Longtao,Chen Zhenyu,Li Guang
- School of Materials and Chemical Engineering,Henan University of Engineering,Zhengzhou 450007,China