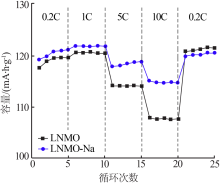
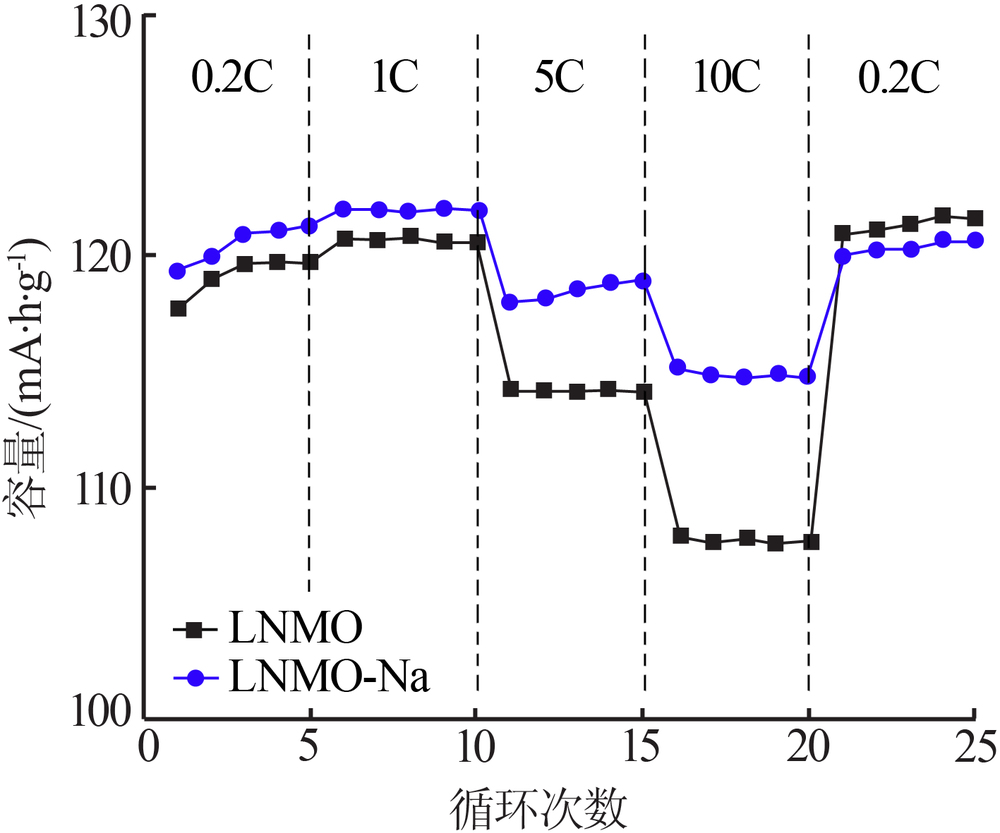
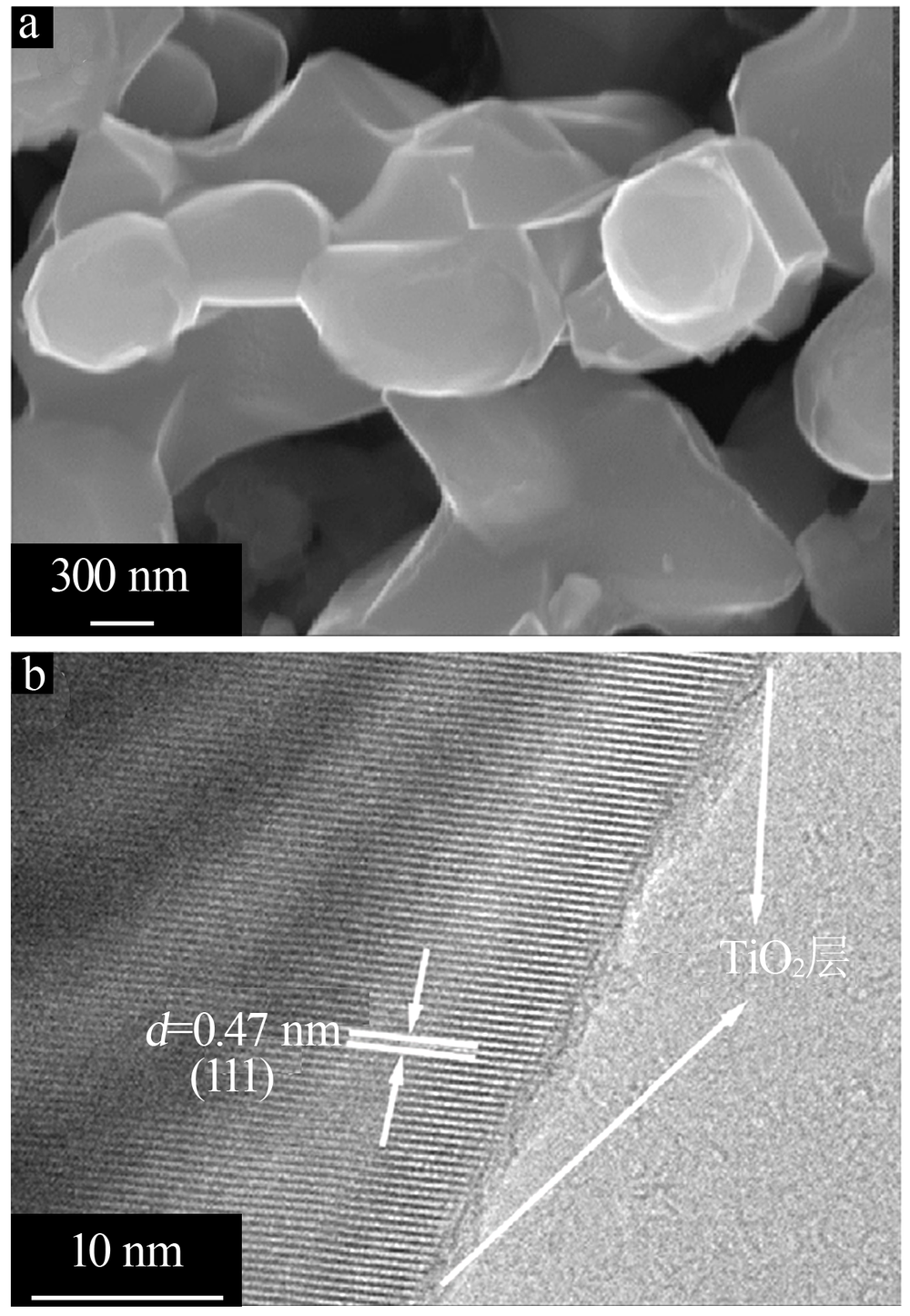
| [1] |
Amine K, Tukamoto H, Yasuda H , et al. A new three-volt spinel Li1+xMn1.5Ni0.5O4 for secondary lithium batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1996,143(5):1607-1613.
|
| [2] |
郅晓科, 叶学海, 赵桢 , 等. LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4正极材料制备及其电化学性能研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2014,46(6):66-68.
|
| [3] |
金彦章, 王永和, 刘强 , 等. 高电压正极材料LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4制备及性能研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017,49(6):45-49.
|
| [4] |
白钢印, 王英 . 掺杂Fe 3+对高电压正极材料LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4结构和性能的影响 [J]. 材料导报, 2015,29(6):15-18.
|
| [5] |
Bini M . Silicon-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as a high-voltage cathode for Li-ion batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2018,320:1-6.
|
| [6] |
Wu W, Guo J, Qin X , et al. Enhanced electrochemical performances of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel in half-cell and full-cell via yttrium dop-ing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017,721:721-730.
|
| [7] |
Feng S, Kong X, Sun H , et al. Effect of Zr doping on LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with ordered or disordered structures[J]. Journal of Alloys and Co-mpounds, 2018,749:1009-1018.
|
| [8] |
邓春晓, 张焕, 高静静 , 等. BPS对LNMO电化学性能的提高及作用机理[J]. 电源技术, 2017,41(2):183-185.
|
| [9] |
Yi T F, Li Y M, Li X Y , et al. Enhanced electrochemical property of FePO4-coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as cathode materials for Li-ion bat-tery[J]. Science Bulletin, 2017,62(14):1004-1010.
|
| [10] |
Liu J, Cheng Y, Fan Q , et al. Tri-functional coating to enhance the capacity retention of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for high power lithium ion bat-tery[J]. Materials Letters, 2018,214:68-71.
|
| [11] |
Deng Y, He L, Ren J , et al. Reinforcing cycling stability and rate capability of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode by dual-modification of coating and doping of a fast-ion conductor[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2018,100:333-344.
|
| [12] |
Xu J, Xia Q, Chen F , et al. Facilely solving cathode/electrolyte in-terfacial issue for high-voltage lithium ion batteries by construct-ing an effective solid electrolyte interface film[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,191:687-694.
|
| [13] |
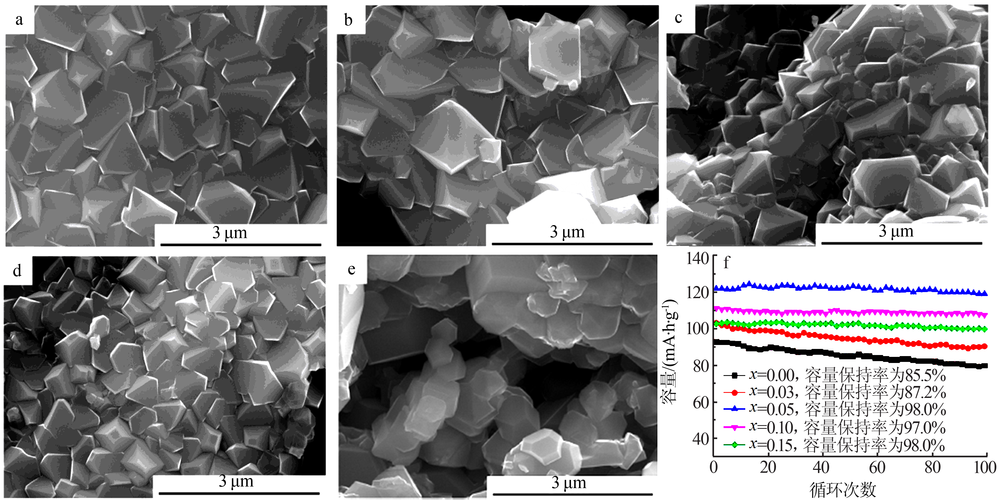
Sun H Y, Kong X, Wang B S , et al. Cu doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5-xCuxO4 (x=0,0.03,0.05,0.10,0.15) with significant improved electro-chemical performance prepared by a modified low temperature solution combustion synjournal method[J]. Ceramics International, 2018,44(5):4603-4610.
|
| [14] |
Wu W, Qin X, Guo J L , et al. Influence of cerium doping on struc-ture and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2017,35(9):887-895.
|
| [15] |
李渊, 刘恒, 徐艺林 , 等. 固相法合成高电压正极材料镍铬锰酸锂[J]. 无机盐工业, 2012,44(4):55-58.
|
| [16] |
Wang J, Chen D, Wu W , et al. Effects of Na+ doping on crystalline structure and electrochemical performances of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 catho-de material[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017,27(10):2239-2248.
|
| [17] |
Luo Y, Li H, Lv T , et al. Fluorine gradient-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel with improved high voltage stability for Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,238:237-245.
|
| [18] |
Jung S H, Kim D H, Brüner P , et al. Extremely conductive RuO2-coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,232:236-243.
|
| [19] |
Tao S, Kong F, Wu C , et al. Nanoscale TiO2 membrane coating spi-nel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for advanced lithium-ion bat-teries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017,705:413-419.
|
| [20] |
Fan Y, Wang J, Tang Z , et al. Effects of the nanostructured SiO2 coat-ing on the performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for high-voltage Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007,52(11):3870-3875.
|
| [21] |
Mou J, Deng Y, He L , et al. Critical roles of semi-conductive LaFeO3 coating in enhancing cycling stability and rate capability of 5 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018,260:101-111.
|
| [22] |
马腾飞, 徐婷婷, 宗意恒 , 等. 高电压正极材料镍锰酸锂的表面包覆及其电化学性能[J]. 常熟理工学院学报, 2018,32(2):3-6.
|
| [23] |
Xu Y H, Zhao S X . Improved electrochemical performance of 5 V spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 microspheres by F-doping and Li4SiO4 coat-ing[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2016,2(3):265-272.
|
| [24] |
Chen Z, Wang C, Xing L , et al. Borate electrolyte additives for high voltage lithium nickel manganese oxide electrode:A comparative study[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,249:353-359.
|
| [25] |
任春燕, 叶学海, 张春丽 , 等. 高电压正极与电解液添加剂相容性研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017,49(5):45-47.
|
| [26] |
Drozhzhin O A, Shevchenko V A . Improving salt-to-solvent ratio to enable high-voltage electrolyte stability for advanced Li-ion batte-ries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018,263:127-133.
|
| [27] |
Zhao D, Wang P, Cui X , et al. Robust and sulfur-containing ingre-dient surface film to improve the electrochemical performance of LiDFOB-based high-voltage electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018,260:536-548.
|