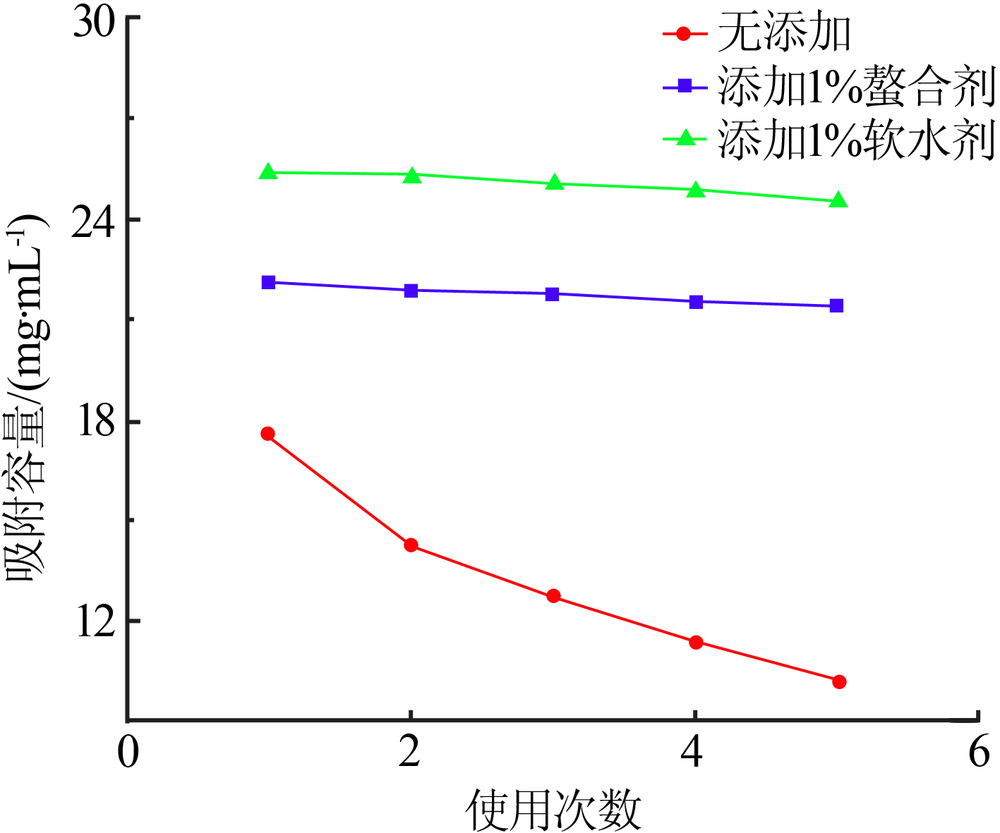
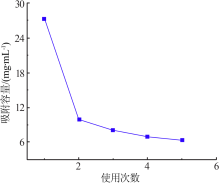
| [1] |
吴伟, 郝文魁, 李晓刚 , 等. 高Cl-环境对M152和17-4PH高强钢应力腐蚀开裂行为的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2018,46(2):105-114.
|
| [2] |
潘旭东, 王向明 . 循环水中氯离子控制及对不锈钢腐蚀机理探讨[J]. 工业水处理, 2013,33(3):14-16.
|
| [3] |
刘海洋, 夏怀祥, 江澄宇 , 等. 燃煤电厂湿法脱硫废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2016,34(1):31-35.
|
| [4] |
余晓利, 潘卫国, 郭士义 , 等. 燃煤电厂湿法烟气脱硫废水零排放技术进展[J]. 应用化工, 2018,47(1):160-164.
|
| [5] |
Ma S C, Chai J, Chen G D , et al. Research on desulfurization waste-water evaporation:Present and future perspectives[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016,58:1143-1151.
|
| [6] |
徐辉, 陈小娟, 龙长江 , 等. 离子交换法制备氨基磺酸镍[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017,49(12):46-49.
|
| [7] |
张弦, 叶春松, 黄建伟 , 等. 高盐废水残余Ca(Ⅱ)的离子交换软化实验[J]. 热力发电, 2018,47(8):66-72.
|
| [8] |
梁博 . 离子交换柱在废水处理中的应用[J]. 合成材料老化与应用, 2015,44(3):117-119.
|
| [9] |
化娜丽, 路帅, 赵东风 , 等. 离子交换去除炼厂难降解废水中氯离子的静态实验研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2015,47(11):66-69.
|
| [10] |
赵玉, 赵德智, 王德慧 , 等. 离子交换树脂吸附净化工业废液研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2018,47(3):584-588.
|
| [11] |
万华, 张正方, 丁宇 , 等. 强碱阴离子交换树脂对乙二醇-水溶液中氯离子的吸附行为及机理[J]. 新疆大学学报:自然科学版, 2010,27(2):222-225.
|
| [12] |
谢子楠, 王蛟, 沈家国 . 工业硫酸锰中钙、镁的净化研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2015,47(5):48-50.
|