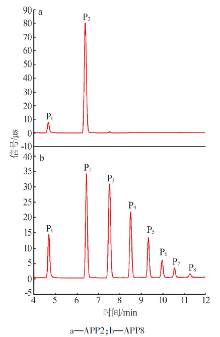
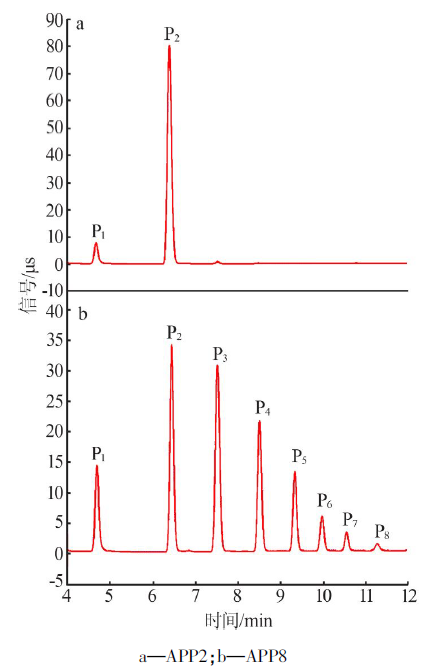
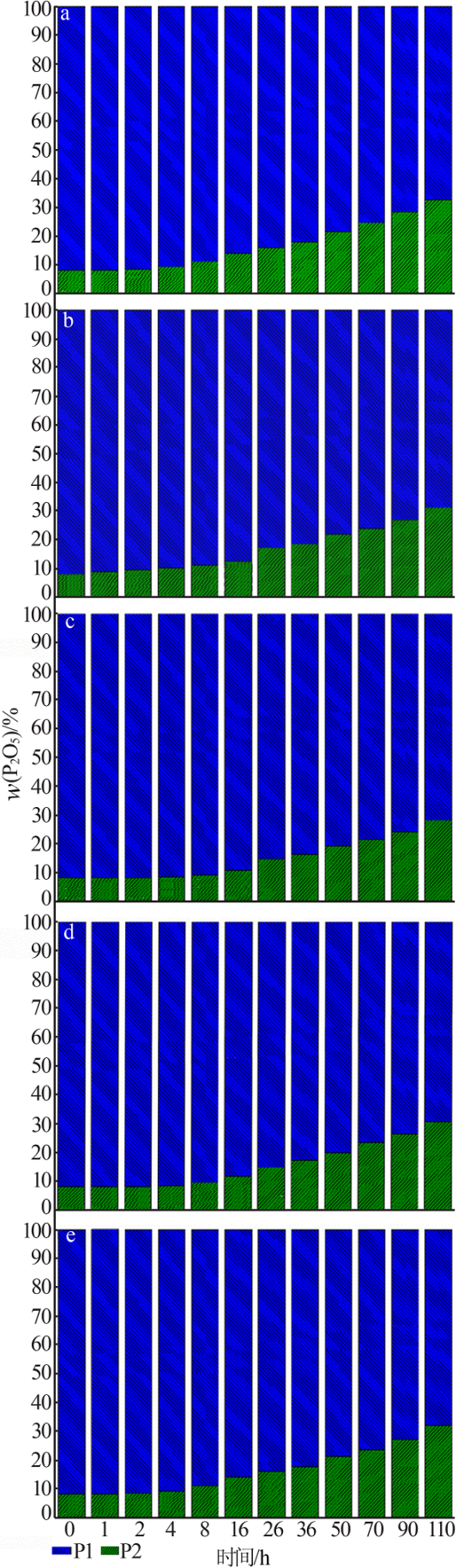
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 72-76.doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2019-0590
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
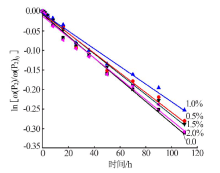
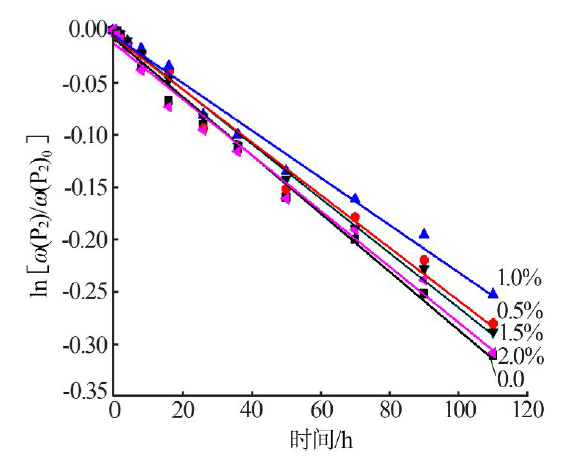
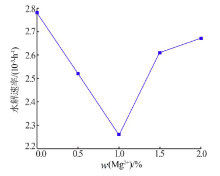
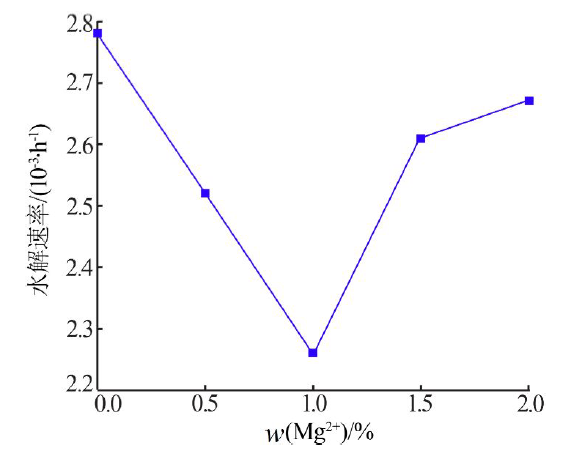
Effect of Mg2+ on hydrolysis of water soluble ammonium polyphosphate
Wang Yan( ),Wang Xinlong,Xu Dehua,Xu Dejun,Yang Jingxu
),Wang Xinlong,Xu Dehua,Xu Dejun,Yang Jingxu
- Engineering Research Center of Comprehensive Utilization and Clean Processing of Phosphorus Resources,Ministry of Education,School of Chemical Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,China
-
Received:2020-04-22Online:2020-10-10Published:2020-11-24
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yan,Wang Xinlong,Xu Dehua,Xu Dejun,Yang Jingxu. Effect of Mg2+ on hydrolysis of water soluble ammonium polyphosphate[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(10): 72-76.
share this article
| [1] | Braun U, Schartel B, Fichera M A, et al. Flame retardancy mechanisms of aluminium phosphinate in combination with melamine polyphosphate and zinc borate in glass-fibre reinforced polyamide 6,6[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2007,92(8):1528-1545. |
| [2] | Annakutty K S, Kishore K. Flame retardant polyphosphate esters:1.Condensation polymers of bisphenols with aryl phosphorodichloridates:synjournal,characterization and thermal studies[J]. Polymer, 1988,29(4):756-761. |
| [3] | 梁文, 王辛龙, 陈建钧, 等. 水溶性聚磷酸铵螯合锌的规律研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019,51(11):20-22. |
| [4] |
Huang R, Wan B, Hultz M, et al. Phosphatase-mediated hydrolysis of linear polyphosphates[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018,52(3):1183-1190.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b04553 pmid: 29359927 |
| [5] | 郑福林, 刘代俊, 陈建钧. 农用聚磷酸铵的制备与表征[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017,49(2):28-30,86. |
| [6] | Engelstad O P, Allen S E. Ammonium polyphosphate and ammonium orthophosphate as sources of phosphorus for Jerusalem artichoke[J]. Alexandria Science Exchange Journal, 2015,36(1):47-57. |
| [7] | 徐保明, 徐思思, 唐强, 等. 水溶性聚磷酸铵的合成工艺进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017,49(4):5-8. |
| [8] | Thilo E, Wieker W. Study of degradation of polyphosphates in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 1961,53(158):55-59. |
| [9] | 谢汶级, 王辛龙, 许德华, 等. 不同pH对焦磷酸铵水解的影响[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019,51(10):28-31. |
| [10] | 王蕾, 邓兰生, 涂攀峰, 等. 聚磷酸铵水解因素研究进展及在肥料中的应用[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2015,30(4):25-27. |
| [11] | McBeath T M, Lombi E, McLaughlin M J, et al. Polyphosphate-fer-tilizer solution stability with time,temperature,and pH[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2007,170(3):387-391. |
| [12] | 杨军芳, 周晓芬, 冯伟. 土壤与植物镁素研究进展概述[J]. 河北农业科学, 2008(3):91-93,96. |
| [13] | Svoboda L H E, Kovárová M. Simplified post-column derivatization method for ion chromatography of linear polyphosphates[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2002,25(10/11):715-718. |
| [14] | Xie W, Wang X, Li Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of various phosphates in water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate[J]. Chromatographia, 2019,82(11):1687-1695. |
| [15] | Williard J W, Farr T D, Hatfield J D. Hydrolysis of ammonium pyro-,tripoly-,and tetrapolyphosphate at 25.deg.and 50.deg[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 1975,20(3):276-283. |
| [16] |
Steveninck V J. The influence of metal ions on the hydrolysis of polyphosphates[J]. Biochemistry, 1966,5(6):1998-2002.
doi: 10.1021/bi00870a030 pmid: 5964701 |
| [17] | Yang J, Kong X, Xu D, et al. Evolution of the polydispersity of ammonium polyphosphate in a reactive extrusion process:Polycondensation mechanism and kinetics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019,359:1453-1462. |
| [1] | Yan Bo,Xie Tian,Zhu Huacheng,Yang Fengming,Wang Fengxia,Chen Yong. Study on process of synthesizing ammonium polyphosphate by microwave heating [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(7): 42-45. |
| [2] | Chen Yanguang,Han Tong,Zhang Yanan,Yang Xiuqi,Han Hongjing,Wang Hao. Process regulation of ZSM-5 zeolite synthesis from hydrolyzed tetraethyl orthosilicate as silicon source in acidic medium [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(7): 88-93. |
| [3] | Chen Yong,Yang Sanke,Xie Tian,Tao Shaocheng,Long Qinglan,Liu Xu. Research on preparation process of water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate with high polymerization rate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(5): 50-52. |
| [4] | Chen Yuerong,Jin Huiming,Yu Liang,Shao Yangyang. Preparation of amorphous Co-Cr-B and catalytic sodium borohydride hydrolysis for hydrogen generation [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(2): 91-96. |
| [5] | Liu Xu,Tang Jianwei,Liu Yong,Hua Quanxian,Wang Baoming. Research and application progress of water-soluble agricultural ammonium polyphosphate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(12): 7-11. |
| [6] | Chen Zhenbang,Yang Shousheng. Aging mechanism and life prediction of ammonium polyphosphate thermal-oxidative acceleration aging [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(3): 20-24. |
| [7] | Sun Haijie,Chen Lingxia,Zhang Yufeng,An Dongdong,Liu Cong. Performance of Co-B/ZrO2 catalyst for hydrogen generation from catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride solution [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(3): 72-76. |
| [8] | Ling Haohan,Wang Xinlong,Xu Dehua,Liang Wen,Xie Wenji. Effect of water soluble ammonium polyphosphate with different degree of polymerization on chelation of magnesium ion [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(12): 20-22. |
| [9] | Lu Ruifang,Wu Jianchun,Liu Chan. Influence of titanyl sulfate solution hydrolysis process on tintreducing power of rutile titanium dioxide [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(12): 44-48. |
| [10] | Liang Wen,Wang Xinlong,Chen Jianjun,Xie Wenji,Leng Xinke,Ling Haohan. Study on law of chelated Zn by water?鄄soluble ammonium polyphosphate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(11): 20-22. |
| [11] | Yang Shengdong,Xu Dehua,Wang Xinlong,Zhang Zhiye. Study on technology of preparing ammonium polyphosphate containing chelated magnesium by in?鄄situ method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(11): 46-49. |
| [12] | Wu Jianchun,Lu Ruifang,Liu Chan,Xin Huijin. Analysis of factors affecting particle size distribution of hydrolyzed metatitanic acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(11): 50-53. |
| [13] | Xie Wenji,Wang Xinlong,Xu Dehua,Liang Wen,Ling Haohan,Leng Xinke,Yang Jingxu. Effect of different pH on hydrolysis of ammonium pyrophosphate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(10): 28-31. |
| [14] | DAI Li-Ming, GENG Xiao-Hong, LIU Jing, MENG Lin, LIU Zhen-Min, ZHENG Dong-Mei. Detection of titanium dioxide content in inferior titanium dioxide by selective compexometric titration [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2016, 48(11): 62-. |
| [15] | YANG Lin, YI De-Lian, WANG Cheng, WU Lin. Analysis on stability of titanium sulfate solution and metatitanic acid size control [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2015, 47(4): 26-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|