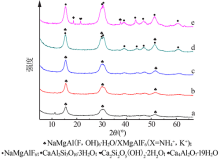
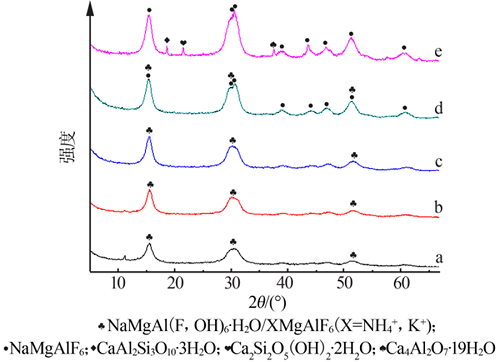
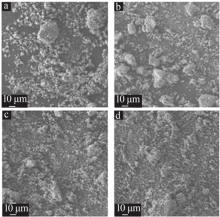
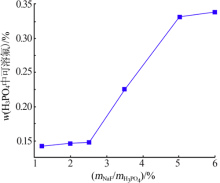
Inorganic Chemicals Industry ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 48-51.doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2020-0253
• Research & Development • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fabrication of industrial grade ammonium dihydrogen phosphate via selective removal of impurities from wet-process phosphoric acid
Wang Zhijuan
- Faculty of Chemistry and Environment Science, Qujing Normal University, Qujing 655000, China
-
Received:2020-10-13Online:2021-04-10Published:2021-04-23
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhijuan. Fabrication of industrial grade ammonium dihydrogen phosphate via selective removal of impurities from wet-process phosphoric acid[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(4): 48-51.
share this article
| [1] | 李新柱, 郭宗端, 贾亮 , 等. 甲醇沉淀法净化湿法磷酸制备工业级磷酸一铵[J]. 无机盐工业, 2016,48(2):40-41. |
| [2] | 王毕德, 丁一刚, 何俊 , 等. 工业磷铵母液制备工业磷酸一铵的工艺研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017,49(10):46-48. |
| [3] | 郑润, 解田, 刘飞 , 等. 磷酸二氢铵应用研究进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2014,46(4):1-3. |
| [4] | Bhagawat L I, Patil V S, Kale B B , et al. Sonoprocessing of LiFePO4 nanoparticles and nanocomposites for cathode material in lithium ion batteries[J]. Polymer Composites, 2016,37(6):1874-1880. |
| [5] | Tan Qiangqiang, Yan Bo, Xu Yuxing , et al. Preparation and electro-chemical performance of carbon-coated LiFePO4/LiMnPO4-positive material for a Li-ion battery[J]. Particuology, 2017,30:144-150. |
| [6] | Joshi J H, Kalainathan S, Kanchan D K , et al. Effect of L-threonineon growth and properties of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate crystal[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020,13(1):1532-1550. |
| [7] | Joshi J H, Kalainathan S, Joshi M J , et al. Crystal growth, spectroscopic, second and third order nonlinear optical spectroscopic studies of L-phenylalanine doped ammonium dihydrogen phosphate single crystals[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020,13(4):5018-5026. |
| [8] | 李军, 金央, 罗建洪 . 用湿法磷酸制工业磷酸二氢铵工艺综述[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2016,31(5):17-18. |
| [9] | 廖晓婷, 李军, 陈明 . 磷酸脲母液制备工业级磷酸二氢铵工艺研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2020,52(4):79-83. |
| [10] | 江善襄 . 磷酸、磷肥和复混肥料[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1999. |
| [11] | 李青, 姚美焕, 王超 , 等. 湿法磷酸两步净化及工业级磷酸二氢铵的制备[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2016(8):23-25. |
| [12] | 庄艳萍 . 湿法磷酸制备工业级磷酸一铵试验研究[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2009,24(5):14-16. |
| [13] | 张胜, 冯克敏, 沈鹏 , 等. 一种磷酸一铵的生产工艺:中国, 107539971A[P]. 2018 -01-05. |
| [14] | 廖吉星, 朱飞武, 彭宝林 , 等. 湿法磷酸生产工业级磷酸一铵联产工业级磷酸二铵的方法:中国, 103011113A[P]. 2013 -04-03. |
| [15] | 曾润国, 刘甍, 魏家贵 . 一种用半水磷酸多段中和直接生产工业级磷酸一铵方法:中国, 106744762A[P]. 2017 -05-31. |
| [16] | 徐魁, 穆劲, 陈彬 . 湿法磷酸直接生产工业级磷酸一铵的方法:中国, 102320585A[P]. 2012 -01-18. |
| [17] | 陈德清, 王娜, 张敏 . 湿法磷酸净化生产工业磷酸一铵研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2016,48(1):38-40. |
| [18] | Xu Dejun, Wan Jiali, Xu Dehua , et al. Chelation of metal ions with citric acid in the ammoniation process of wet-process phosphoric acid[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019,98(3):665-675. |
| [19] | 岳海荣, 应建康 . 络合沉淀法脱除湿法磷酸中铝镁杂质的统计分析[J]. 无机盐工业, 2009,41(6):51-53. |
| [20] | 黎铉海, 李华生, 潘柳萍 , 等. 氢氟酸在湿法磷酸净化中的应用研究[J]. 广西大学学报:自然科学版, 2009,34(1):54-56. |
| [1] | Tang Yuzhong,Zheng Shuaifei,Zhang Qingxi,Xue Zhiqiang,Qin Jishan. Study on preparation of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate from phosphoric acid waste solution of chemical polishing of aluminum and aluminum alloy [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(5): 88-92. |
| [2] | Yin Wei,Huang Jin,Xie Tian,He Bingbing. Experimental study on high efficiency decomposition of phosphate rock by phosphoric acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(9): 34-36. |
| [3] | Wang Xiaoxiong,Zhang Jiangang,Zhang Wenjing,Chen Ye. Removal of calcium chloride from crude phosphoric acid by hydrochloric acid method [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(8): 17-19. |
| [4] | Wang Xiheng,Sun Wenzhe. Research progress on fluorine recovery technology in wet process phosphoric acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(8): 25-29. |
| [5] | Yan Bo,Xie Tian,Zhu Huacheng,Yang Fengming,Wang Fengxia,Chen Yong. Study on process of synthesizing ammonium polyphosphate by microwave heating [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(7): 42-45. |
| [6] | Chen Yong,Yang Sanke,Xie Tian,Tao Shaocheng,Long Qinglan,Liu Xu. Research on preparation process of water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate with high polymerization rate [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(5): 50-52. |
| [7] | Wang Baoming,Lü Zhonghao,Li Huiyong,Liu Yong,Hua Quanxian,Tang Jianwei. Research progress on preparation of urea phosphate with wet-process phosphoric acid [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2020, 52(11): 1-5. |
| [8] | Shao Yixin,Zhang Zeqiang,Huang Chaode,Sun Hualin. Research on influencing factors of industrial phosphoric acid decomposing phosphate rock and properties of by-products [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(6): 49-52. |
| [9] | XIONG Xing, ZHANG Bi-Jiang, XU De-Jun, ZHANG Zhi-Ye, RUAN Yong-Gang, YANG Lin, ZHOU Xue-Ke, WANG Xin-Long. Study on effects of cooling rate on ammonium dihydrogen phosphate′s metastable zone [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2016, 48(6): 48-. |
| [10] | LIU Fei, JIE Tian, ZHENG Run, YANG Fan. Study on influencing factors of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate crystallization process [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2016, 48(3): 46-. |
| [11] | LIU Fei, LI Tian-Xiang, JIE Tian, SHI Lian-Jun. Study on purification of purified wet-process phosphoric acid [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2016, 48(2): 42-. |
| [12] | ZHANG Hai-Yan, MING Da-Zeng, JI Xiao-Ling, YANG Jin. Analysis on de-fluorination reaction principle of wet process phosphoric acid [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2015, 47(1): 9-. |
| [13] | ZHOU Jing, BAI Ren-Liu, Zhou-Jun-Hong, WANG Jue, LUO Jun, JIA Shuang-Zhu. Preparation of high-quality potassium dihydrogen phosphate from wet-process phosphoric acid by extraction method [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2014, 46(9): 21-. |
| [14] | WENG Yan-Ling, JIN Yang, LI Jun, JIA Xu-Hong, WU Hao-You. Study on demulsification of emulsification extraction of wet process phosphoric acid [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2014, 46(5): 27-. |
| [15] | XIN Yang-Yang, YE Shi-Chao, LI Jun-Hong. Experimental extraction study of Kühni column with dispersed network [J]. INORGANICCHEMICALSINDUSTRY, 2014, 46(5): 42-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|