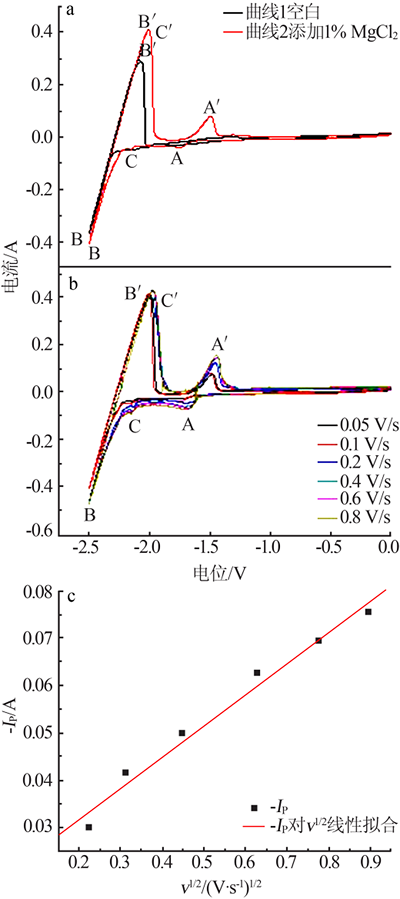
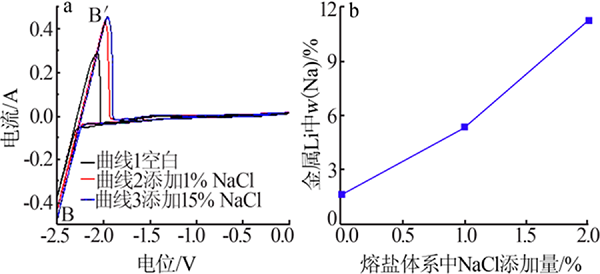
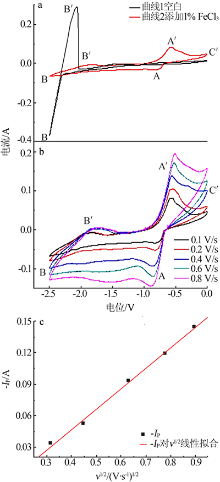
| [1] |
汪家铭 . 金属锂生产应用及市场分析[J]. 盐业与化工, 2006,36(1):44-46.
|
| [2] |
陈悦娣 . 电池级金属锂生产工艺探讨[J]. 新疆有色金属, 2014(5):74-76.
|
| [3] |
杨凤丽, 王浩然, 杨少华 , 等. LiF-SrF2-SrO 熔盐体系中Sr 2+电化学行为的研究 [J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2016,7(5):33-36,66.
|
| [4] |
Sun Xiuyun, Lu Guimin, Fan Shudi . Electrochemical mechanism of electrolysis codeposition of Mg-Sr alloy in molten salt[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014,24:1629-1634.
|
| [5] |
Castrillejo Y, Martinez A M, Pardo R , et al. Electrochemical behaviour of magnesium ions in the equimolar CaCl2-NaCl mixture at550 ℃[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1997,42(12):1869-1876.
|
| [6] |
Martı′nez A M, Børresen B, Haarberg G M , et al. Electrochemical behavior of Mg 2+ ions in MgCl2-CaCl2-NaCl molten salt [J]. Journalof the Electrochemical Society, 2004,151(7):508-513.
|
| [7] |
Martı′nez A M, Børresen B, Haarberg G M , et al. Electrodeposition of magnesium from the eutectic LiCl-KCl melt[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2004,34:1271-1278.
|
| [8] |
刘兆庭, 路贵民, 于建国 . NaCl-KCl-CaCl2熔盐体系中Mg 2+在Mo电极上的阴极过程 [J]. 有色金属:冶炼部分, 2018,12:27-32.
|
| [9] |
Kouji Yasuda, Toshiyuki Nohira, Ogata Y H , et al. Electrochemical window of molten LiCl-KCl-CaCl2 and the Ag +/Ag reference electrode [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005,51:561-565.
|
| [10] |
申淼 . 电化学方法去除LiCl-KCl体系微量杂质的研究[D]. 上海:华东理工大学, 2012.
|
| [11] |
张永健 . 镁电解生产工艺学[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2006: 326-331.
|
| [12] |
Liu Zhaoting, Lu Guimin, Yu Jianguo . Effects of Fe(Ⅲ) on MgCl2 electrolysis and its cathodic processes on W electrodes[J]. Ionics, 2019,25:3945-3952.
|
| [13] |
Li Hui, Zhang Lisheng, Liang Jinglong , et al. Electrochemical behavior of Fe3O4 in NaCl-CaCl2 melts[J]. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 2019,17(10):1-10.
|
| [14] |
马尚润, 朱福兴, 李开华 . 流水线镁电解过程中杂质Fe控制技术[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2019,42(10):73-81.
|
| [15] |
朱福兴, 马尚润, 姜宝伟 . 镁电解杂质元素对液镁汇集的影响及控制[J]. 轻金属, 2019(1):48-53.
|
 ),Li Quan1,2,Huo Yan1,2,Li Mingzhen1,2,Zhang Huifang1,2,Pang Quanshi3,Wu Zhijian1,2(
),Li Quan1,2,Huo Yan1,2,Li Mingzhen1,2,Zhang Huifang1,2,Pang Quanshi3,Wu Zhijian1,2( )
)